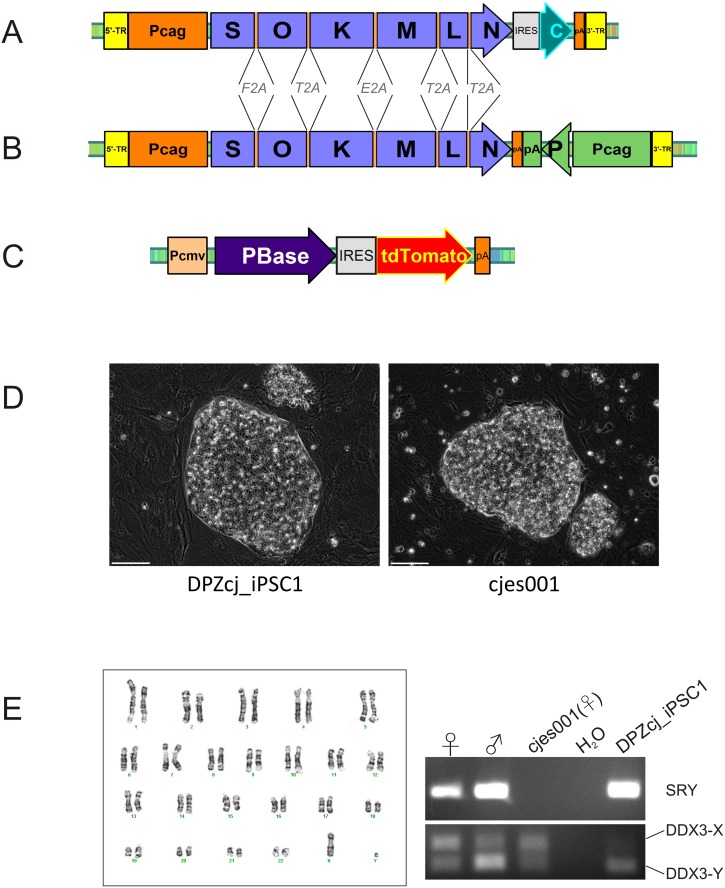
Fig 1. Reprogramming constructs and morphology of marmoset monkey iPS cells.
A) and B) Constructs containing the reprogramming cassette. Expression of the reprogramming factors is driven by the CAG promoter (Pcag). Stop codons of the first five reprogramming factors were substituted with coding sequences for 2A peptides (F2A, T2A, E2A). IRES, internal ribosomal entry site; pA, poly A signal; 5ˈ-TR, 5ˈ-terminal repeat; 3ˈ-TR, 3ˈ-terminal repeat; S, SOX2; O, OCT4; K, KLF4; M, c-MYC; L, LIN28; N, NANOG; C, Cerulean; P, puromycin resistance gene. C) Expression of the Transposase (PBase) is driven by the Cytomegalovirus promoter (Pcmv). D) Morphology of iPS cell colonies. The morphology of the generated iPSCs (DPZcj_iPSC1) and the marmoset ES cell line cjes001 are indistinguishable from each other. Bars = 100 μm E) Karyotype analysis of DPZcj_iPSC1. Karyogram showing a normal Karyotype 46, XY (left). Right: PCR analysis confirming the male genotype. Primers used amplify a fragment of the Sex-determining region Y gene (SRY) and the X or Y chromosome-linked genes DDX3 (DDX3-X, DDX3-Y). The analysis was done with genomic DNA from a newborn female marmoset (♀), a newborn male marmoset (♂), an established female ES cell line (cjes001) and the generated iPS cell line DPZcj_iPSC1. Water was used as negative control (H2O).