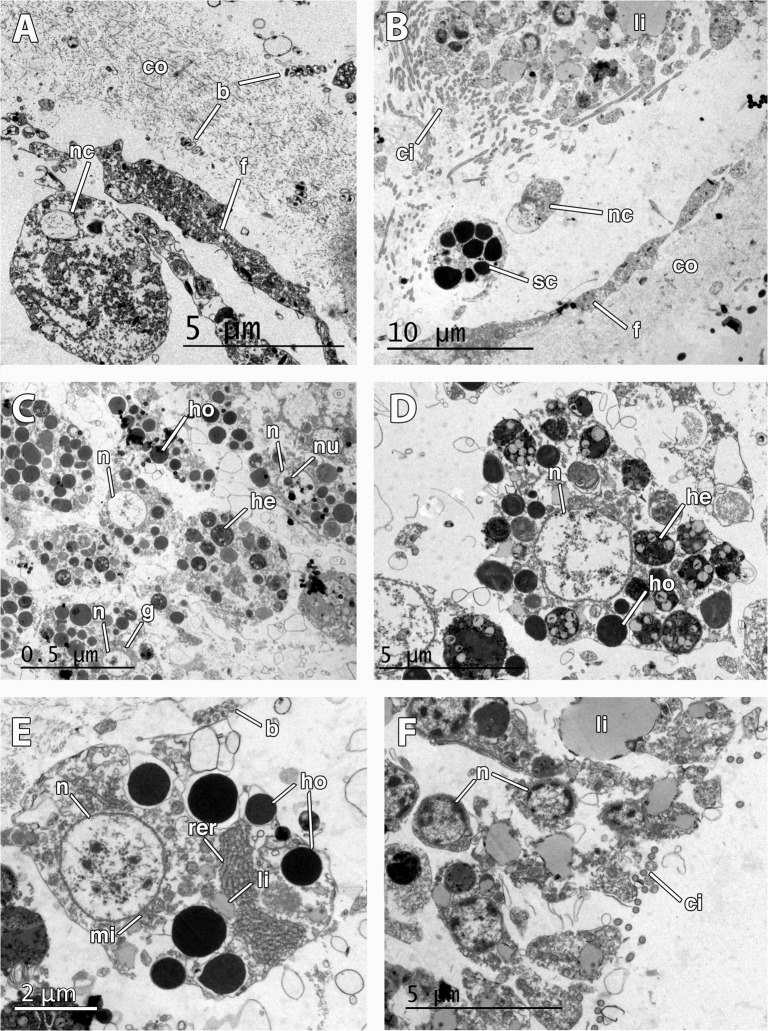
Fig 6. Ultrastructure of the embryo and larva of Mycale laevis.
A. Cellular follicle (f) and collagen layer (co) surrounding the embryo. Note the presence of a nurse cell (nc) within the lumen of the embryonic follicle and symbiotic bacteria (b) lying in the collagen layer. B. Posterior end of the larva showing ciliated cells (ci) prior to the bare area, and lipid droplets (li) in the cells. Note that nurse (nc) and spherulous cells (sc) have crossed the follicle (f) and are found within the lumen. C. Round nucleolated (nu) cells in the mid part of the larva showing homogeneous (ho) and heterogeneous (he) yolk, and Golgi apparatus (g). Note the round nucleus of the cells (n). D. Close up of nucleated (n) larval cell showing homogeneous (ho) and heterogeneous (he) yolk. E. Detail of nurse cell outside the embryo showing large rough endoplasmic reticulum (rer), non-nucleolated nucleus (n), several mitochondria (mi), and many homogenous yolk platelets (ho). Note the bacteria (b) in the mesohyl. F. Larval ciliated (ci) cells in the posterior end showing large lipid droplets (li).