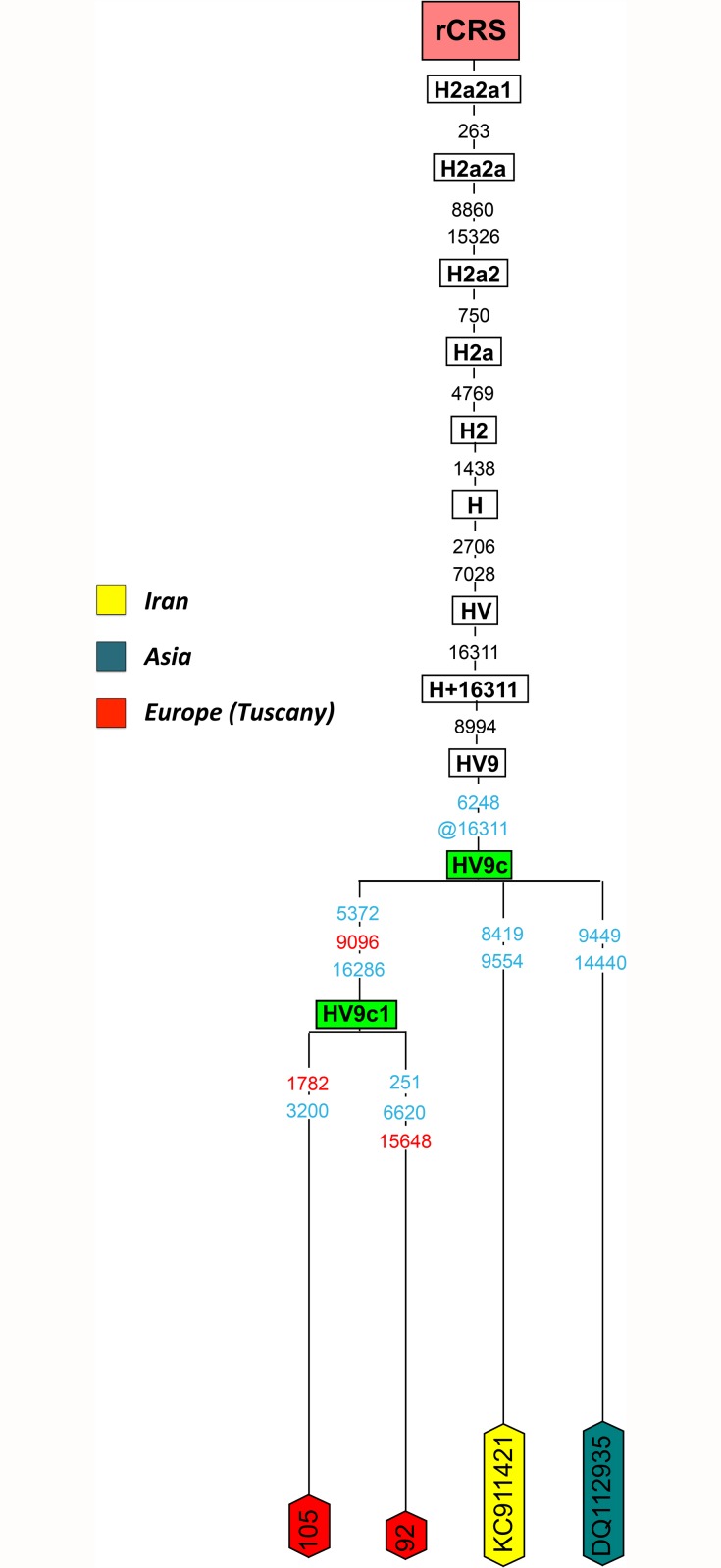
Fig 1. Maximum parsimony tree of haplogroup HV9c.
All the specifications below are common for all the phylogenetic trees built for the present study, although not all of them necessarily concur in the same tree. The position of the revised Cambridge Reference Sequence (rCRS) is indicated for reading off sequence motifs [15]. Mitochondrial DNA variants are indicated along the branches of the phylogenetic tree. Mutations are transitions unless a suffix A, C, G, or T indicates a transversion. Other possible suffixes indicate insertions (.) and deletions (d). The prefix ‘@’ indicates a back or missing mutation. Mutational hotspot variants at positions 16182, 16183, and 16519, indels at 515–524, additions at 16193 as well as variation around position 310 and length or point heteroplasmies were not considered for the phylogenetic reconstruction. Polymorphisms colored in blue at the tips of the phylogeny are private variants while polymorphisms colored in red are private variants not described in PhyloTree Build 16. Haplogroup green boxes indicate a new haplogroup or a difference with respect to haplogroup definitions in PhyloTree Build 16.