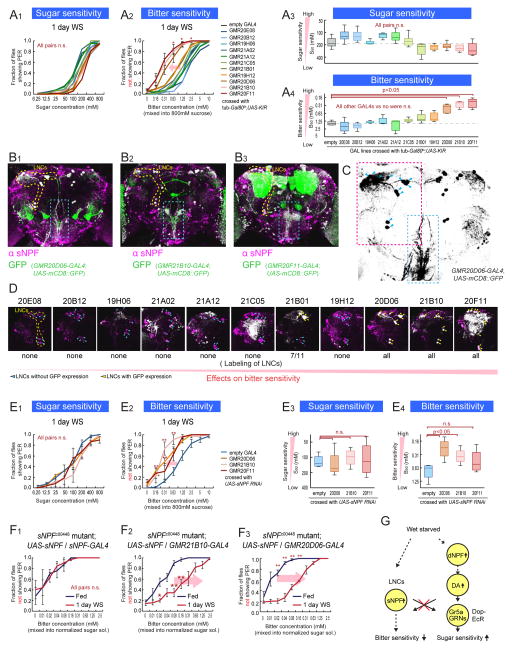
Figure 4. Subsets of sNPF Neurons Regulate Bitter Sensitivity During Starvation.
(A) Sugar and bitter sensitivity of flies with genetic silencing of different subsets of sNPF neurons. For this experiment, w-; UAS-KIR2.1; tub-Gal80ts flies were crossed with the indicated GAL4 lines or promoterless BDP-GAL4 flies (empty-GAL4). Flies were incubated at 31 °C for 2 days to inactivate Gal80ts before experiments. (B) Representative confocal projections of whole mount brains of sNPF promoter GAL4 lines crossed with UAS-mCD8::GFP flies and stained with anti-sNPF precursor antibody. Overlap of signals are shown in white color. LNCs are surrounded by yellow dotted lines. Axonal projection of LNCs are surrounded by blue dotted boxes. (C) Structure of LNCs. Blue arrowheads indicate cell bodies of LNCs. (D) Enlarge representative confocal projections of dorso-posterior side of the sNPF promoter GAL4 lines crossed with UAS-mCD8::GFP. LNCs are surrounded by yellow dotted line in the left panel. White color indicates the locations with overlap of GFP and anti-sNPF signals (Raw GFP signals in green are not shown to clarify the locations with the overlap. See Figure S4 for raw data). Blue arrowheads and yellow arrowheads indicate LNCs without and with GFP expression, respectively. (E) Sugar and bitter sensitivity of flies with UAS-sNPFR RNAi driven under the control of sNPF promoter GAL4 lines or BDP-GAL4 flies (No-GAL4). (F) Bitter sensitivity measured with normalized-sugar PER assays in sNPF mutant flies with genetic rescue of sNPF expression in different subsets of neurons (w-; sNPFc00448; UAS-sNPF crossed with w-; sNPFc00448; sNPF-GAL4 (F2) or w-; sNPFc00448; GMR21B10-GAL4 (F3)). See also Figure 3C2–3 for comparison. n>5 for all experimental groups. (G) Schematic summarizing results. See also Figure S4.