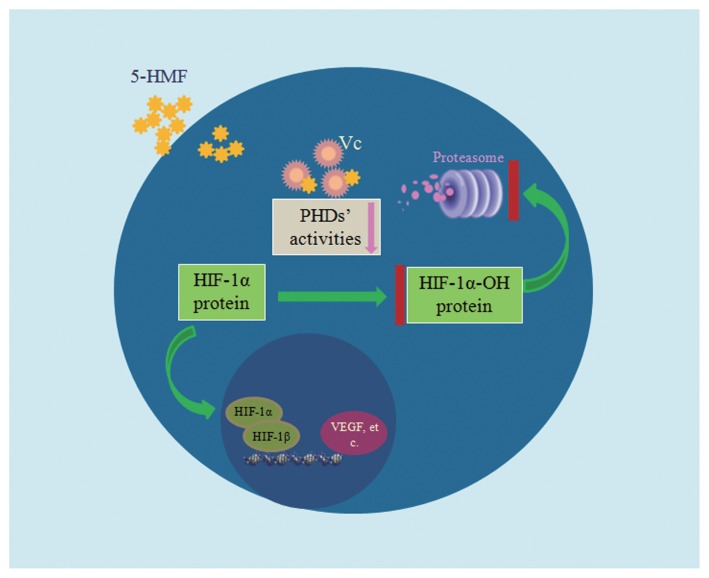
Figure 7.
Model depicting the role of 5-HMF in stabilizing HIF-1α. 5-HMF enters cells in a dose-dependent manner. Then, 5-HMF rapidly interacts with VC and thereby reduces the VC content. PHD activities are declined because of the reduction in VC. HIF-1α hydroxylation is inhibited because of the reduction of PHD activity, and thus, HIF-1α cannot be degraded through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Therefore, the HIF-1α protein is stabilized and then translocates into the nucleus. In the nucleus, HIF-1α combines with HIF-1β to form the heterodimeric transcription factor HIF-1, which regulates the transcription of its downstream genes, such as VEGF.