FIG 3.
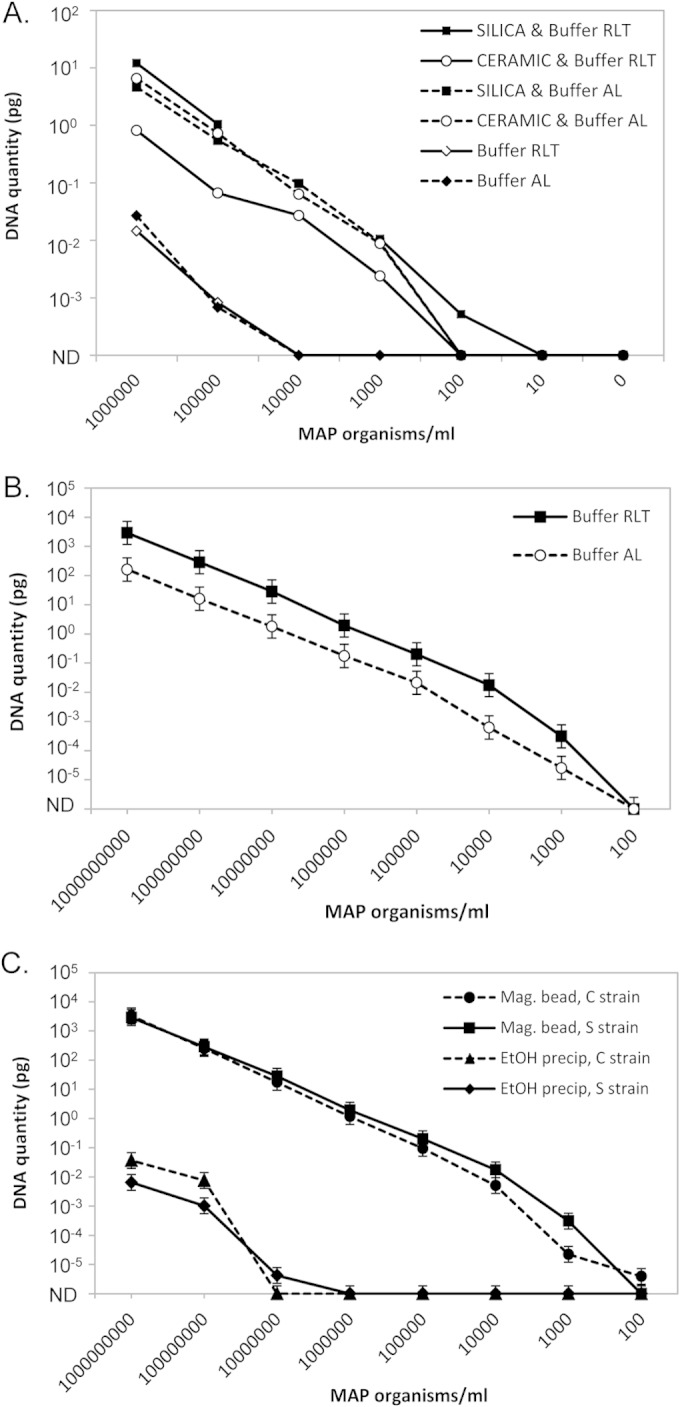
Detection of MAP in liquid culture media by qPCR. (A) Pilot study to test the feasibility of using magnetic bead isolation of MAP from liquid culture media. M7H9C medium samples were spiked with known quantities of sheep strain MAP (106 to 101 MAP/ml culture medium) and a control with no MAP (0); n = 1/treatment and MAP concentration. (B) Comparison of buffer RLT to buffer AL. M7H9C medium samples were spiked with known quantities of sheep strain MAP (108 to 101 MAP/ml culture medium); n = 4/treatment and MAP concentration. Predicted means ± SEM from the REML linear mixed model. Buffer RLT was significantly different from buffer AL (P < 0.001). (C) Comparison of the standard ethanol precipitation method to the optimized magnetic bead DNA isolation method performed on samples spiked with known quantities of either cattle or sheep strain MAP (108 to 101 MAP/ml culture medium); n = 4/treatment and MAP concentration. Predicted means ± SEM from the REML linear mixed model. The optimized magnetic bead method was significantly different from the ethanol precipitation method (P < 0.001). ND, not detected.
