Fig. 4.
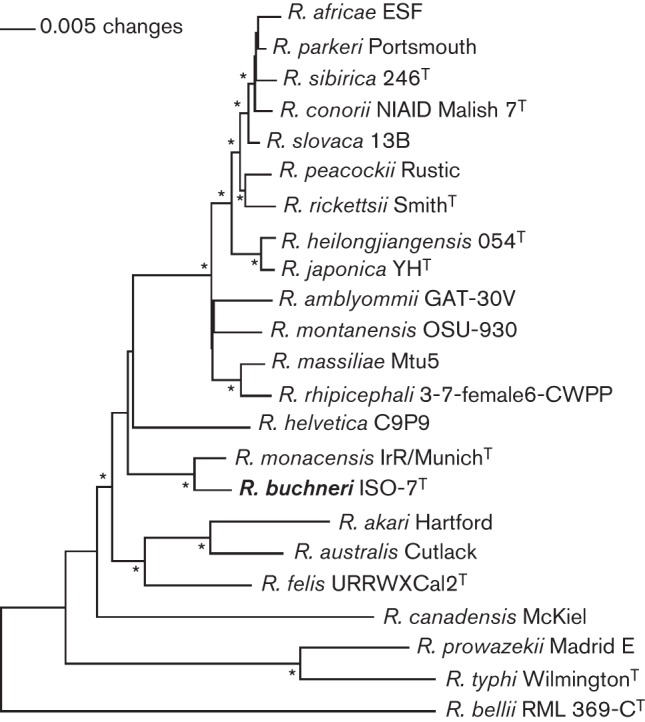
Phylogram showing that ISO7T and ‘R. monacensis’ are closely related and reside in a clade separate from other rickettsiae. Neighbour-joining tree is based on amino acid sequences of 11 concatenated proteins (Table S1). Protein sequences were concatenated in the direction of amine to carboxyl group in the order of proteins HtpG, InfB, RpoA, RpoB, PolA, ThrS, GroEL, GyrB, RecA, DnaE and Pnp. Sequences were aligned using muscle (Edgar, 2004) set at default parameters. The alignments were transferred into the paup* (Swofford, 2002) program as nexus files, and maximum-likelihood and neighbour-joining trees were reconstructed. Trees were rooted by making the outgroup (Rickettsia bellii) paraphyletic with respect to the ingroup. The robustness of clade designations was tested with a full heuristic search and 1000 bootstrap replicates, and nodes with asterisks are supported at values of ≥99 %.
