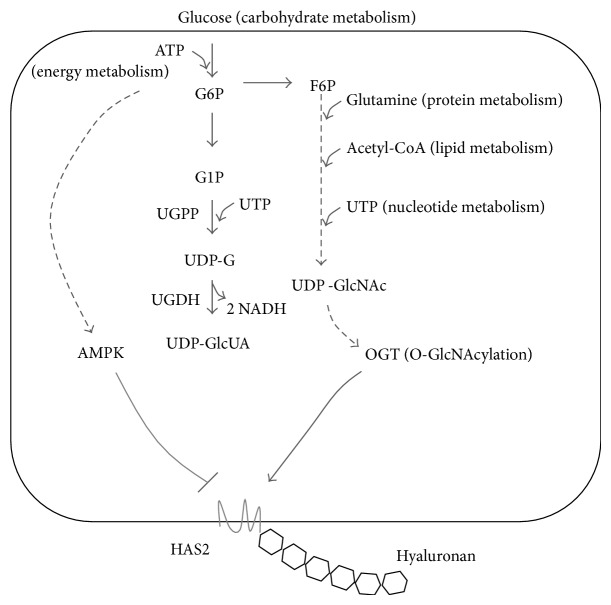
Figure 1.
HA precursors biosynthesis and main HAS2 regulation in SMCs. Glucose enters in the cells and is phosphorylated by ATP. Glucose 6 phosphate (G6P) can be converted into glucose 1 phosphate (G1P), UDP-glucose (UDP-G), and UDP-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcUA) by the enzymatic reactions catalyzed by UDP-G pyrophosphorylase (UGPP) and UDP-G dehydrogenase (UGDH). This latter reaction produces 2 NADH. G6P can enter in the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway, which starts from fructose 6 phosphate (F6P) and, in several steps, produces UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc). These steps depend on carbohydrates, energy, proteins, lipids, and nucleotides metabolisms making UDP-GlcNAc a master nutrient sensor. AMPK in condition of ATP depletion (or activation by metformin) inhibits HAS2 by threonine 110 phosphorylation. An increment of UDP-GlcNAc induces O-GlcNAcylation of serine 221 of HAS2 by OGT. This glycosylation strongly stabilizes HAS2 protein avoiding its degradation.