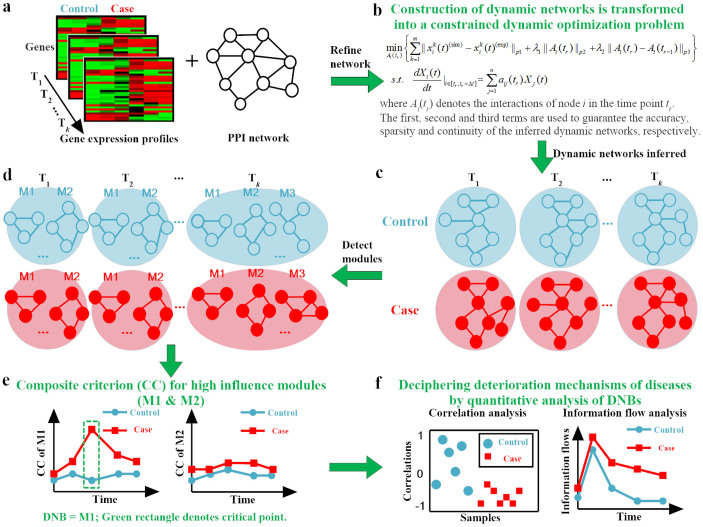
Figure 1. Overview of the proposed paradigm for making early diagnoses and unveiling the deterioration mechanisms of complex diseases.
(a) Comparative time-series gene expression profile of binary conditions (Control vs. Case) was generated using the high-throughput technologies. Rows are genes and columns samples. Prior knowledge of PPI network was integrated with the high-throughput data to construct dynamic networks. (b) The further network inference using the ODE-based dynamic optimization method. The framework of network construction is depicted in Supplementary Figure S1. (c) Comparison of the inferred dynamic networks between the control and case conditions. (d) Modules were detected in the temporary network. (e) High-influence modules that appeared in each time point for both the control and case conditions were selected to identify DNBs using the composite criterion (CC). The framework of DNB identification is shown in Supplementary Figure S2. (f) Quantitative analyses of DNBs, including the correlation and information flow analysis, were employed to decipher the deterioration mechanisms of diseases.