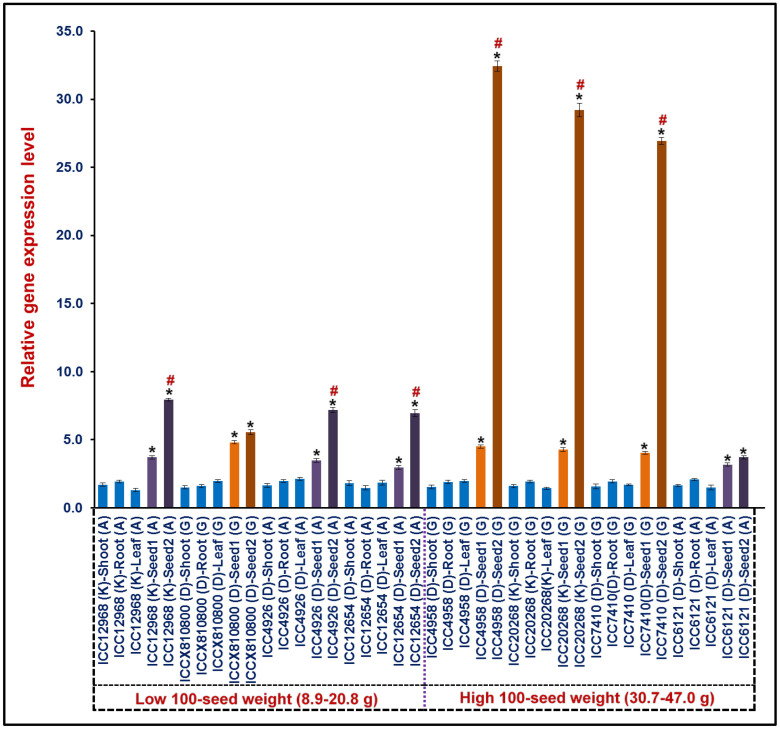
Figure 8. Differential expression profiling of a strong SW-associated regulatory SNP-containing ERF TF gene in three different vegetative (shoot, root and leaf) and two seed developmental stages (S1 and S2: Seed development stages 1 and 2 occurring at 10–20 and 21–30 days after podding, respectively) of eight low (ICC 12968, ICCX-810800, ICC 4926 and ICC 12654 with 100 seed weight: 8.9–20.8 g) and high (ICC 4958, ICC 20268, ICC 7410 and ICC 6121 with 30.7–47.0 g) seed weight contrasting chickpea genotypes as well as parents of mapping population using quantitative RT-PCR assay.
The elongation factor-1 alpha gene was used as an internal control in the RT-PCR assay to normalize the expression values across different tissues/developmental stages of chickpea genotypes and mapping parents. The bars indicate mean (± standard error) of three independent biological replicates with two technical replicates for each sample used in RT-PCR. *Significant differences in gene expression at seed developmental stages of genotypes as compared to leaf at p ≤ 0.01 (LSD-ANOVA significance test). #Significant differences in gene expression between S1 and S2 seed developmental stages of genotypes at p ≤ 0.001 (LSD-ANOVA significance test). The ‘G' and ‘A' SNP-alleles identified in the cis-acting element of ERF TF gene possibly regulating seed weight in desi (D) and kabuli (K) chickpea genotypes are represented.