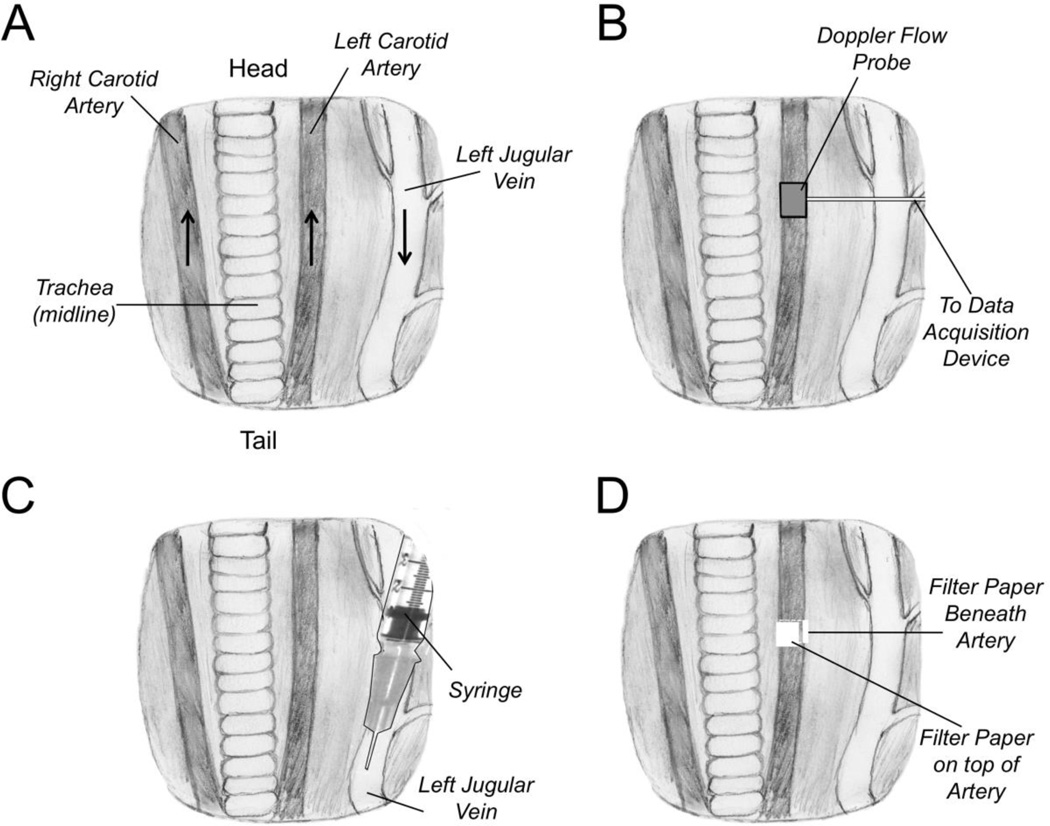
Figure 1. Ferric Chloride Carotid Artery Thrombosis Model.
(A) Anatomy of ventral surface of the mouse neck showing the relative positions of the carotid arteries and jugular vein to the trachea, which runs along the midline. The positions of the animal’s head and tail relative to the drawing are indicated. The black arrows indicate the direction of blood flow in the major vessels. (B) A Doppler flow probe is placed on the carotid artery to monitor blood flow. (C) Anticoagulant compounds to be tested are administered through an intravenous injection into the jugular vein in the direction of blood flow (toward the heart). (D) Pieces of filter paper (two total) saturated with ferric chloride solution are applied beneath and on top of the carotid artery