Figure 1.
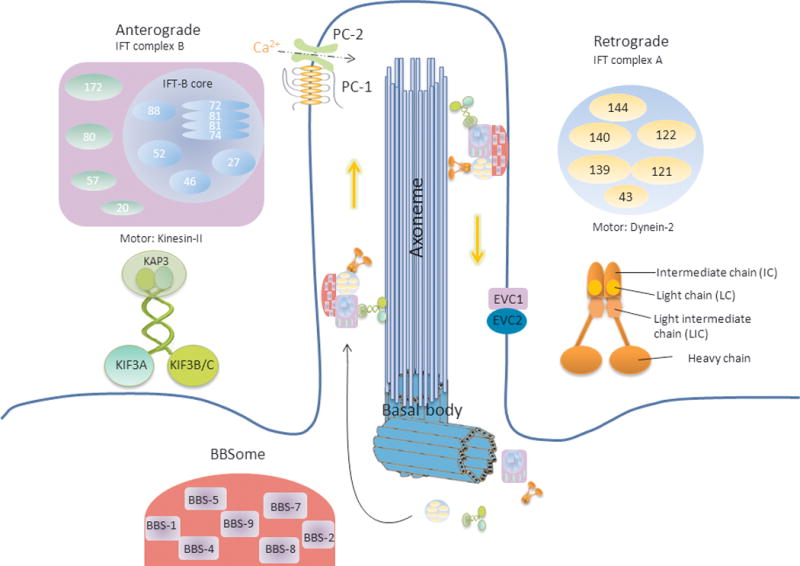
The primary cilium and ciliary proteins (adapted from (28, 87, 234, 235)). The structure of primary cilia is conserved throughout evolution with a basal body (“mother” centriole) and 9 peripheral MT doublets (the axoneme). The Ift-A contains 6 known proteins (Ift144, Ift140, Ift139, Ift122, Ift121 and Ift43) and in charge of retrograde transport (from ciliary tip back to the cell body) with cytoplasmic dynein-2 as motor. Ift-B contains 14 known proteins (Ift20, Ift22, Ift25, Ift27, Ift46, Ift52, Ift54, Ift57, Ift70, Ift74/Ift72, Ift80, Ift81, Ift88 and Ift172) and is involved in anterograde transport (from the base to ciliary tip) with heterotrimeric kinesin-II as motor. Ift81 and Ift74/72 form a tetrameric complex and interact with Ift88, Ift52, Ift46 and Ift27 formed the core of complex B. Besides Ift motors and Ift complexes, BBS proteins are also important for cilia formation and maintenance. Seven highly conserved BBS proteins (BBS1, BBS2, BBS4, BBS5, BBS7, BBS8 and BBS9) formed BBSome. Evc and Evc-2 are located at the basal body and the base of the axoneme. Other proteins like OFD, NEK, Nephrocyustins and MKS proteins are found localized in the basal body. And mutation of these proteins caused diseases.
