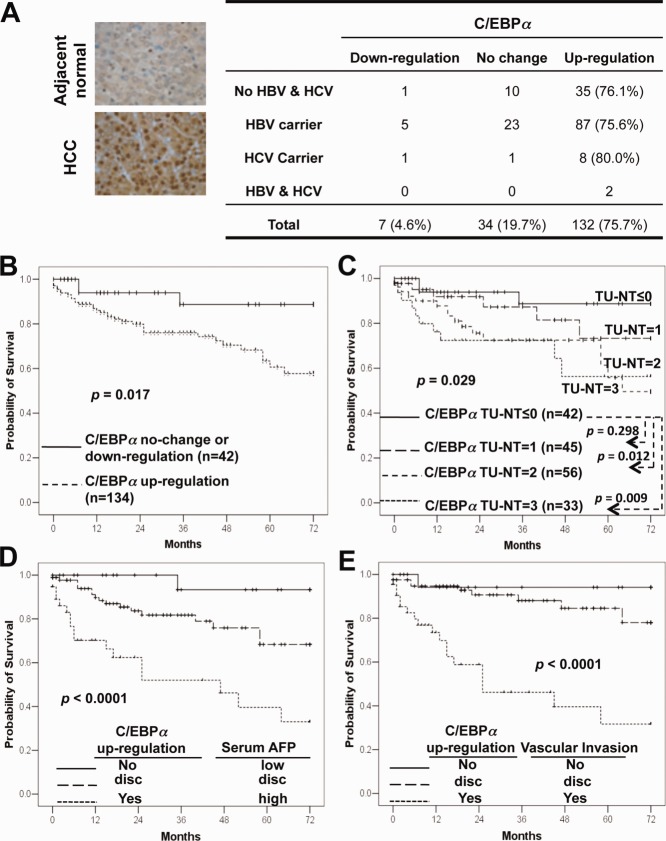
Figure 1.
Up-regulation of C/EBPα in human primary HCC tissues predicted poorer patient survival. (A) The C/EBPα protein was determined by immunohistochemical staining in HCC tissue microarrays and is summarized in the right panel. (B) A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that the patients with upregulated C/EBPα had poorer overall survival. (C) The HCC patients were ranked into four different groups according to the difference between C/EBPα expression in tumor (TU) and in nontumor (NT) tissues, with 0 for no difference and 3 for the highest up-regulation. The number of patients analyzed in each group and P values are indicated. (D,E) Kaplan-Meier curves showed the overall survival of HCC patients subgrouped by C/EBPα and serum AFP level (D) or C/EBPα and vascular invasion (E). Disc, discordant risk assessments: high C/EBPα expression and low risk predicted by AFP (<300 ng/mL)/vascular invasion or vice versa. Abbreviations: HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus.