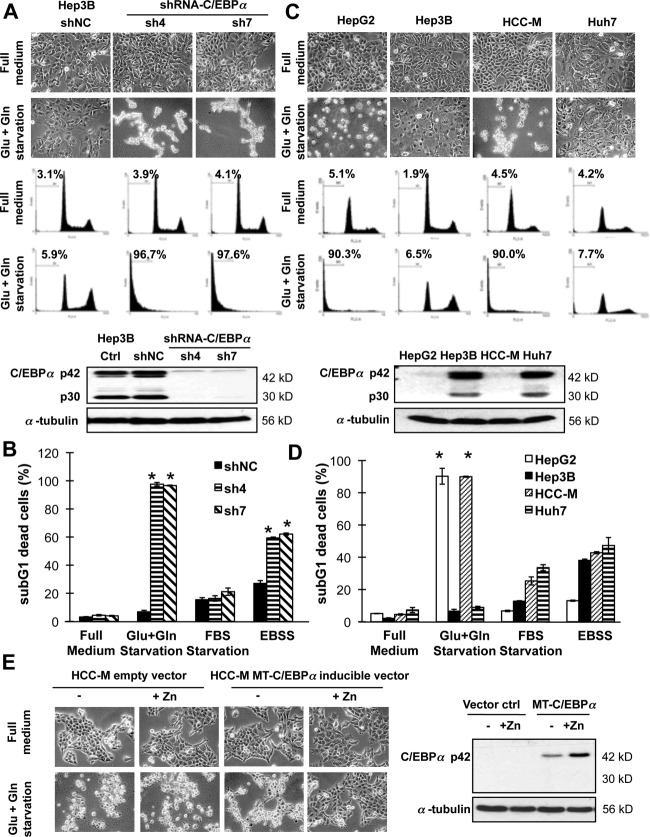
Figure 3.
Hepatocarcinoma cells were protected from energy starvation–induced cell death by C/EBPα. (A) The stable C/EBPα-expressing shNC control cells and C/EBPα–silenced cells (sh4 and sh7) were starved in glucose- and glutamine-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (Glu+Gln starvation) for 2 days. Cell images are shown in the upper panel, followed by cell cycle profiles with the proportion of sub-G1 dead cells indicated as mean ± standard deviation. Western blotting in the lower panel shows the expression of C/EBPα. (B) Cells were starved in glucose- and glutamine-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium, fetal bovine serum–free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium, or fetal bovine serum– and amino acid–double free Earle's Balanced Salt Solution medium for 2 days. (C,D) The C/EBPα-expressing Hep3B and Huh7 and C/EBPα-deficient HepG2 and HCC-M cells were starved as above. (E) Overexpression of C/EBPα using a metallothionein inducible promoter system (induced by 100 µM zinc chloride) in C/EBPα-deficient HCC-M cells resulted in partial protection against starvation-induced cell death. *P < 0.05 compared with cells cultured in full medium. Abbreviations: FBS, fetal bovine serum; EBSS, Earle's Balanced Salt Solution; MT, metallothionein.