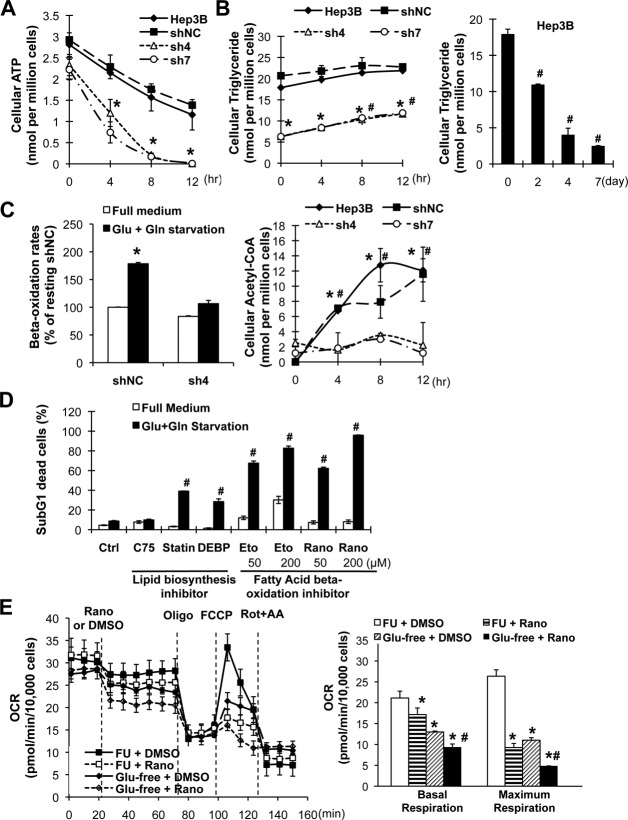
Figure 4.
Lipid catabolism was essential for C/EBPα-mediated protection against energy starvation. Cells expressing C/EBPα (Hep3B and shNC) and C/EBPα-silenced stable cells (sh4 and sh7) were starved in glucose- and glutamine-free medium. The intracellular levels of adenosine triphosphate (A) and triglyceride (B) were determined in a time course. (C) Fatty acid beta-oxidation rates in Hep3B and sh4 cells were determined after 2-hour starvation. Intracellular levels of acetyl-coenzyme A were determined as in A. (D) The Hep3B cells were either pretreated with the liposynthesis inhibitor C75 (5 µg/mL), simvastatin (statin, 10 µM), and diethylum-belliferyl phosphate (50 µM) for 2 weeks before starvation or treated with the fatty acid beta-oxidation inhibitor etomoxir and ranolazine in starvation medium for 3 days. Dead cells were determined by sub-G1 assay as above. *P < 0.05 compared with the corresponding Hep3B and shNC cells of the same time point, #P < 0.05 compared with unstarved cells. (E) Oxygen consumption rates in Hep3B shNC cells were determined by Seahorse mitochondrial stress analysis, under basal conditions and in response to the indicated inhibitors (n = 4). Basal and maximum respiration rates are summarized in the right panel. *P < 0.05 compared with resting cells, #P < 0.05 compared with the corresponding starved cells. Abbreviations: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CoA, coenzyme A; DEBP, diethylum-belliferyl phosphate; Eto, etomoxir; Rano, ranolazine; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; FCCP, fluorocarbonyl cyanide phenylhydrazone; Rot+AA, rotenone and antimycin A; FU, full medium; OCR, oxygen consumption rate.