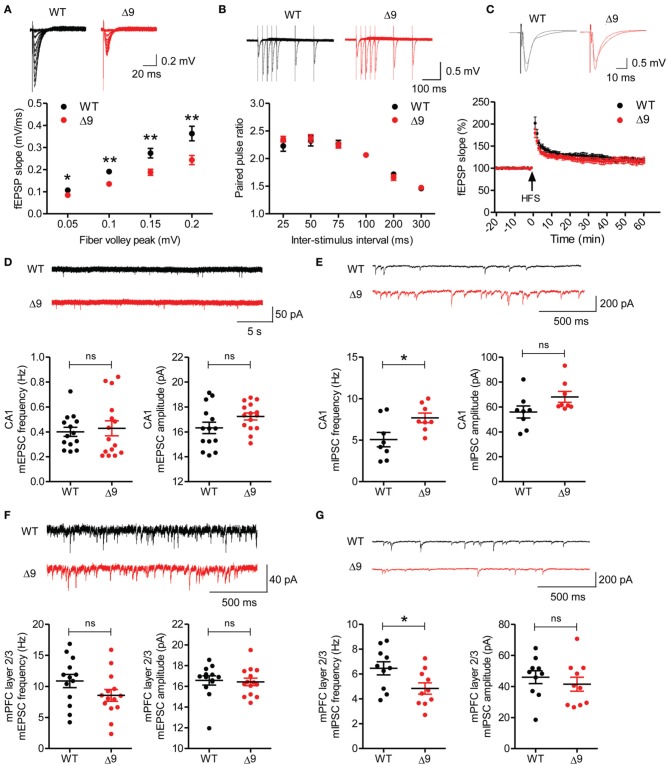
Figure 3.
Reduced excitatory transmission and increased mIPSC frequency in the Shank3Δ9 hippocampus, and decreased mIPSC frequency in the Shank3Δ9 mPFC. (A) Reduced excitatory synaptic transmission at Shank3Δ9 hippocampal SC-CA1 synapses (P19–25), as revealed by plots of fEPSP slopes against fiber volley amplitudes (input–output). Inset, representative traces. N = 9 cells from three mice for WT and Δ9. (B) Normal paired-pulse facilitation at Shank3Δ9 SC-CA1 synapses (P19–25). N = 9 cells from three mice for WT and Δ9. Inset, representative traces. (C) Normal LTP induced by high-frequency stimulation (HFS) at Shank3Δ9 SC-CA1 synapses (P21–24). Inset, representative trace before and after stimulus. N = 8 slices from four mice (WT), seven slices from three mice (Shank3Δ9). (D) Normal frequency and amplitude of mEPSCs in Shank3Δ9 CA1 pyramidal cells (P19–22). N = 14 cells from three mice (WT), 15 cells from three mice (Shank3Δ9). (E) Increased frequency and normal amplitude of mIPSCs in Shank3Δ9 CA1 pyramidal cells (P23–27). N = 8 cells from four mice (WT), eight from three mice (Shank3Δ9). (F) Normal frequency and amplitude of mEPSCs in layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in the prelimbic region of the mPFC in Shank3Δ9 mice (P39–45). N = 13 cells from three mice (WT), 14 cells from three mice (Shank3Δ9). (G) Decreased frequency and normal amplitude of mIPSCs in Shank3Δ9 mPFC prelimbic layer 2/3 pyramidal cells (P39–54). N = 10 cells from four mice (WT), 10 from three mice (Shank3Δ9). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ns, not significant, Student's t-test. Data represent mean ± standard error.