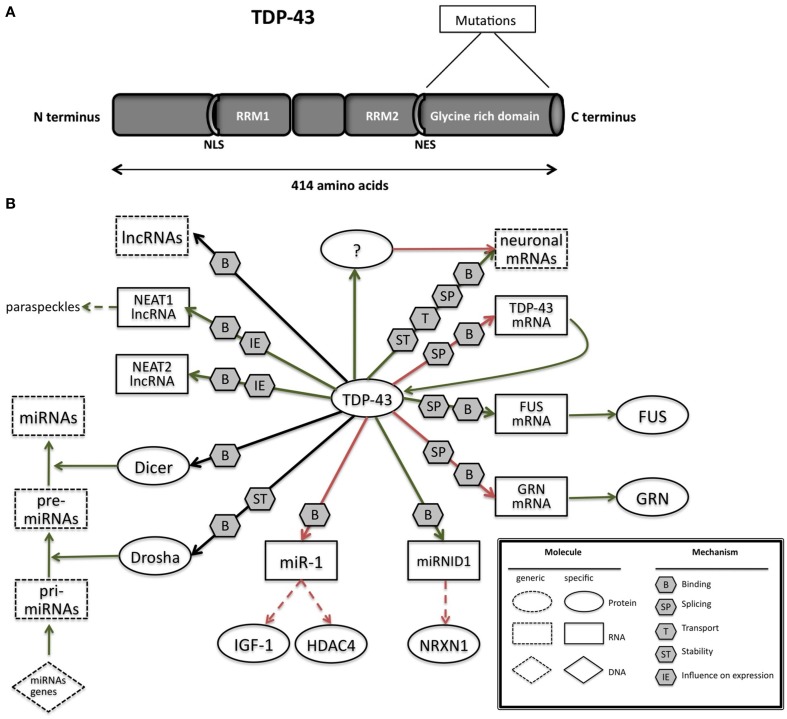
Figure 2.
(A) TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) contains two RNA-recognition motifs (RRM1 and RRM2), a carboxy-terminal glycine-rich domain, a bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS), and a nuclear export signal (NES). Mutations are mainly located in the glycine-rich domain. (B) The network of interactions of TDP-43 with proteins and RNAs. Green arrows indicate binding interactions or processes that result in activation or increased expression. Red arrows indicate binding interactions or processes that result in inhibition of activity or reduced expression. Black arrows indicate binding interactions or processes whose result can be either positive or negative. Dashed arrows indicated indirect processes. Symbols as in Legend. lncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; HDAC4, histone deacetylase 4; NRXN1, neurexin 1; TDP-43, TAR DNA binding protein; FUS, fused in sarcoma; GRN, progranulin; NEAT1, nuclear-enriched autosomal transcript 1; NEAT2, nuclear-enriched autosomal transcript 1.