Figure 1.
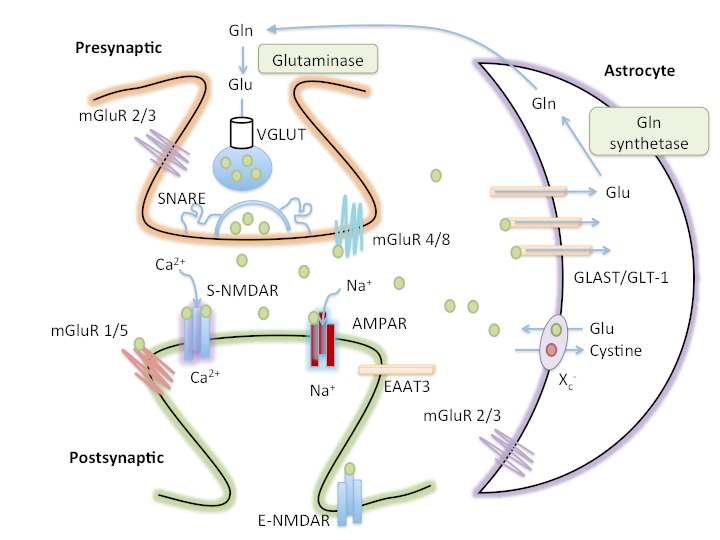
The tripartite glutamate synapse. In the presynaptic neuron, glutamine (Gln) is converted to glutamate (Glu) by glutaminase and packaged into synaptic vesicles by the vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT). SNARE complex proteins mediate the fusion of vesicles with the presynaptic membrane. Astrocytes also release glutamate via the cystine-glutamate antiporter (Xc−). Following release into the extracellular space, glutamate binds to presynaptic (mGluR2/3 and mGluR4/8), synaptic (S-NMDAR and AMPAR) and peri-/extra- synaptic (mGluR1/5 and E-NMDAR) glutamate receptors. Glutamate is cleared from the synaptic space through excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs) on neighboring astrocytes (GLAST and GLT-1) and, to a lesser extent, on neurons (EAAT3). Glutamate is converted to glutamine by glutamine synthetase within the astrocyte before being transported to presynaptic neurons, thereby completing the glutamate-glutamine cycle.
