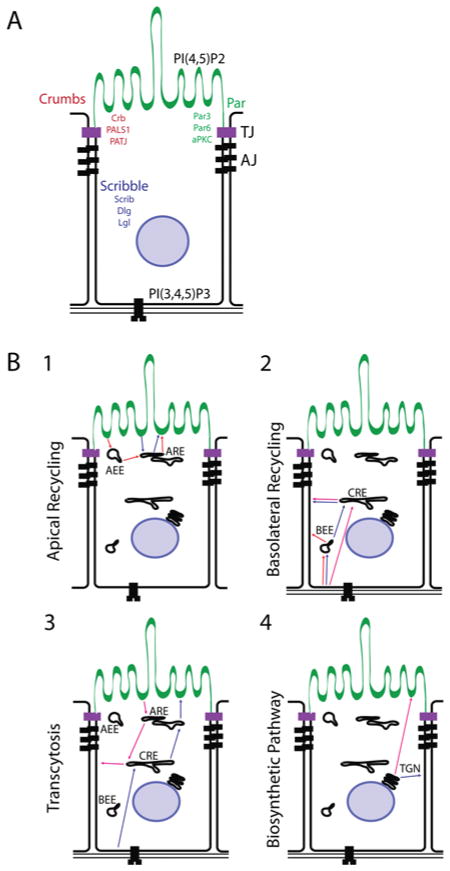
Figure 2. Polarity complexes and routes of polarized transport in epithelial cells.
(A) PIP2 is enriched on the apical PM domain, whereas PIP3 is found pre-dominantly on the basolateral domain. The Par3 protein, part of the apical PAR polarity complex, is localized to the tight junction. Upon the activation of the preformed Par6–aPKC complex by Cdc42, Par6–aPKC is recruited to Par3, where it forms the Par3–Par6–aPKC (PAR) polarity complex and marks the separation of the apical domain from the basolateral. Par6 recruits the CRB complex, which acts as a regulator of the formation and maintenance of the tight junction. The SCRIB complex is recruited by cadherin signalling at sites of cell–cell contacts, and mediates the formation of the basolateral domain. (B) (1) In the apical recycling pathway, cargo is endocytosed from the apical PM domain, and recycled back to the apical domain. (1) Cargo can be transported directly to the ARE, and then be returned directly from the ARE back to the apical PM domain. (2) Cargo can be transported first to the AEE, where it is passed along to the ARE, and then returned to the apical PM. (2) Basolateral recycling occurs when cargo is recycled from and back to the basolateral PM domain. (1) Proteins can be endocytosed to the BEEs and returned directly back to the basolateral PM. (2) Alternatively, cargo can be endocytosed to the BEE, after which it is transported to the CRE, which returns it to the basolateral PM. (3) Finally, cargo can be transported directly to the CRE, and returned to the apical PM. (3) Transcytosis is the transport of cargo from one PM domain to the other. The best-studied pathway of transcytosis is basolateral to apical trans-cytosis. (1) Cargo is internalized from the basolateral PM to the CRE (sometimes via the BEE), which sorts it to the ARE, and releases the cargo on the apical PM. (2) Apical to basolateral transcytosis occurs via the internalization of apical cargo to the ARE (sometimes via the AEE), which sorts the cargo to the CRE. The CRE then directs the cargo to the basolateral PM. (4) Newly synthesized proteins are transported via the biosynthetic pathway from the TGN to either the apical or basolateral domains. These pathways sometimes use endosomal sorting intermediaries; however, direct transport from the TGN to the PM also occurs.