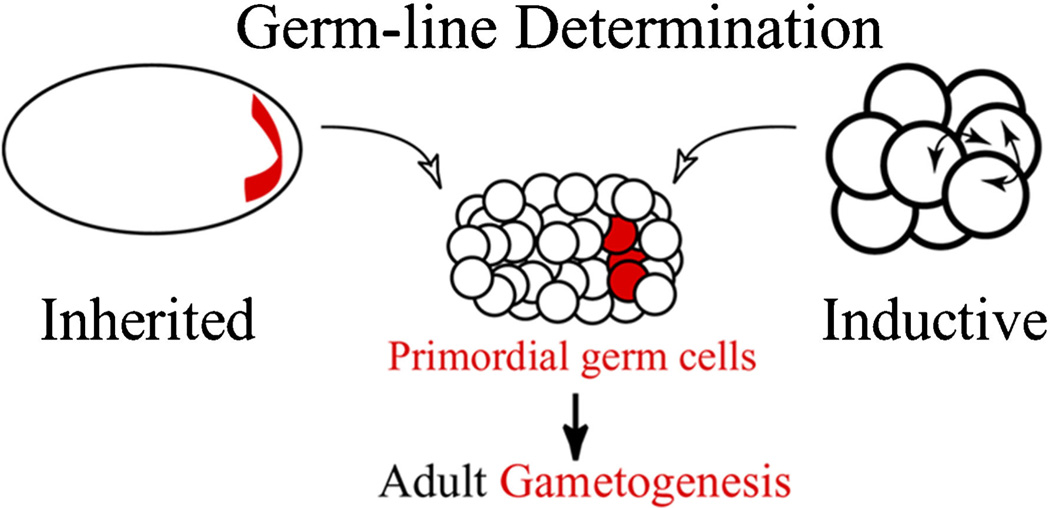
Figure 1.
Inherited versus inductive germline determination. Embryos have two different strategies to determine their primordial germ cells. Inherited mechanisms rely largely on localized maternal determinants that, when acquired by cells of the embryo, assign the fate of a germline to those cells. In contrast, inductive mechanisms rely on intercellular inductive interactions that are interpreted by the cells to acquire a germline fate. Although each mechanism is distinct in principle, they converge on activation of a similar core gene set for maintenance and differentiation of germ cells. These elements include Vasa, Nanos, and Piwi (shown in red).