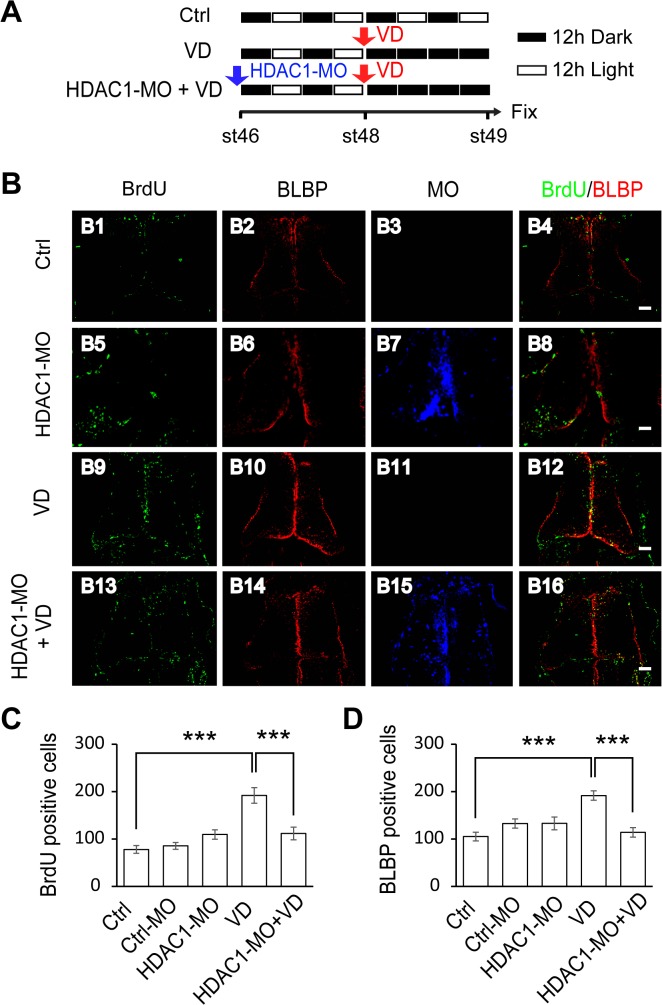
Fig 5. Visual deprivation rescues the decrease in proliferative cells by HDAC1 knockdown.
(A). A cartoon showing that stage 46 tadpoles were placed in a 12h/12h dark light incubator for control, or put into a dark box after 48 hours for VD, or electroporated with HDAC1-MO and placed in a dark box after 48 hours for HDAC1-MO+VD. Tadpoles were incubated with BrdU for immunostaining at stage 49. (B) Fluorescent images showing representative BrdU- and BLBP-labeled cells in control (B1-B4), HDAC1-MO (B5-B8), VD (B9-B12) and HDAC1-MO+VD (B13-B16) tadpoles. Scale: 50 μm. (C-D). Quantification data revealed that visual deprivation increases the number of BrdU- (C) and BLBP-labeled cells (D) and HDAC1-MO knockdown blocked VD-induced increase of proliferative cells. (BrdU: Ctrl, 78.0 ± 8.3, N = 5, Ctrl-MO, 85.4 ± 7.1, N = 5, HDAC1-MO, 109.5 ± 9.8, N = 6, VD, 191.8 ± 16.4, N = 4, HDAC1-MO+VD, 111.6 ± 13.5, N = 5; BLBP: Ctrl, 105.2 ± 9.2, N = 5, Ctrl-MO, 132.6 ± 9.7, N = 5, HDAC1-MO, 133.0 ± 13.5, N = 6, VD, 191.7 ± 9.9, N = 4, HDAC1-MO+VD, 114.0 ± 10.1, N = 5; ***p<0.001).