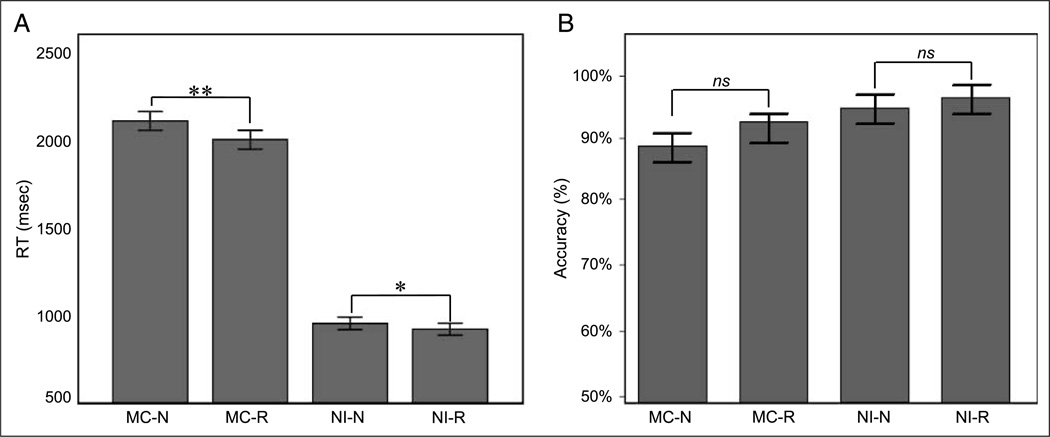
Figure 1.
Behavioral changes underlying RP during MC and NI. (A) RT during both the MC and the NI conditions were significant lower in the repeat compared with the novel trials. RP effects are larger for the MC compared with the NI conditions. (B) Accuracy differences between novel and repeated trials were not significant in both the MC and NI conditions. MC-N = mathematical calculation, novel; MC-R = mathematical calculation, repeat; NI-N = number identification, novel; NI-R = number identification, repeat.