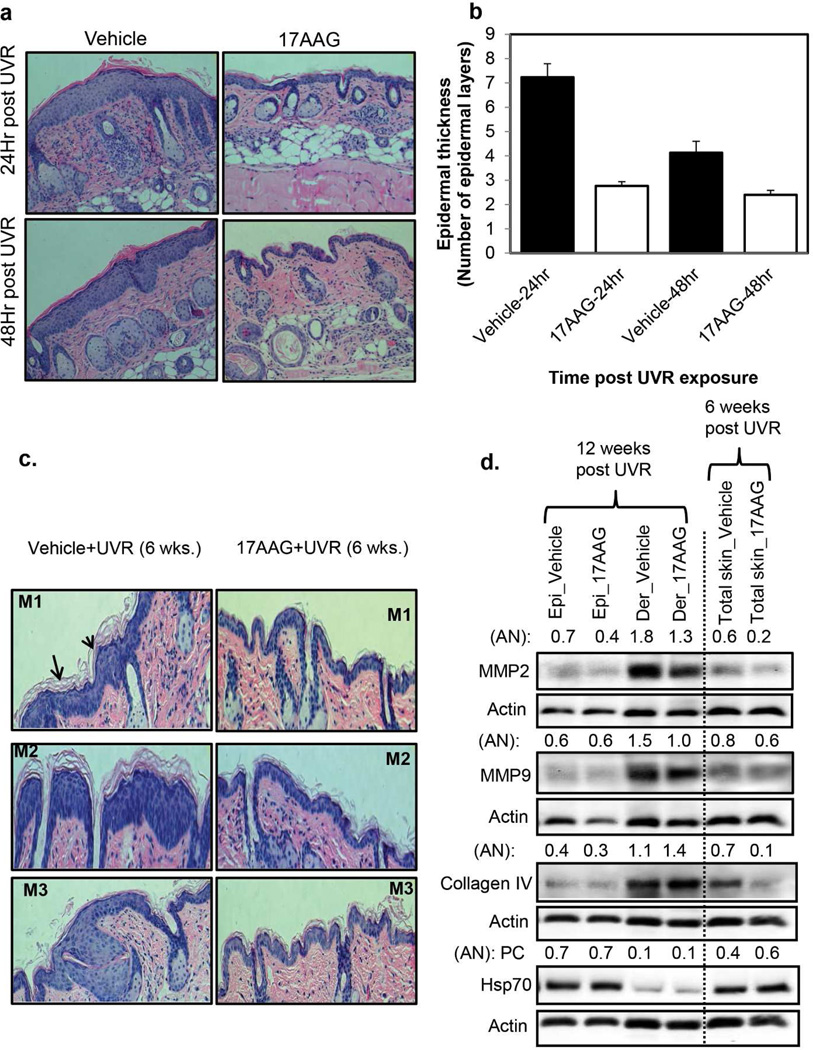
Figure 4. 17AAG-caused inhibition of UVR-induced hyperplasia in SKH1 mice accompanied by decreased expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs).
Groups of SKH-1 mice (n=3) were exposed either four times to UVR (4kJ/m2) or 6 and 12 weeks (2kJ/m2) thrice weekly (Monday, Wednesday, and Friday). Vehicle or 17AAG (500 nmol) was applied post each UVR exposure. (a,b) The mice were sacrificed at 24 h and 48 h after the fourth UVR exposure. For histochemistry, skin specimen were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin for 24 h and embedded in paraffin for sectioning. The figure 4a and b illustrate epidermal hyperplasia and epidermal thickness respectively in vehicle and 17AAG treated SKH-1 mice. Each value in Figure b is the mean±SE of 10 measurements per section of two samples from each mouse. (c) In another experiment, mice were sacrificed at 24 h post 6 and 12 weeks UVR exposures. The figure 4c illustrates epidermal hyperplasia in vehicle and 17AAG treated SKH-1 mice. (d) Expression levels of MMP-2, MMP-9, Collagen IV, and Hsp70 in epidermis, dermis and total skin at 6 and 12 weeks post UVR exposures (pooled samples, n=3). AN: arbitrary number of the quantitation of the Western blots. Epi: epidermis. Der: dermis, M1, M2 and M3 are sections from different mice. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results.