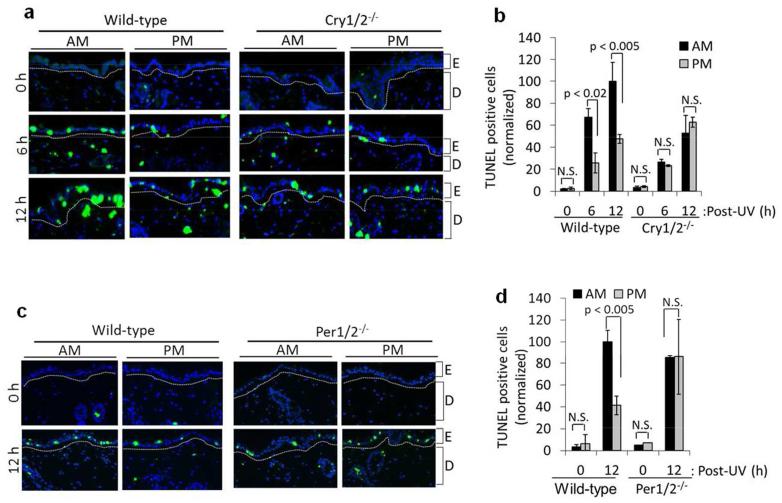
Figure 2.
Circadian regulation of UV-induced sunburn apoptosis in mouse skin. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images of TUNEL assay for the detection of apoptotic cells in the skin of UV-irradiated mice with the C57BL/6 background. Mice were maintained in an LD12:12 cycle and shaved 1 day before irradiation. Both wild-type and Cry1/2−/−mice were irradiated with UV (4000 J/m2) either at ZT21 (4AM) or ZT09 (4PM), and skin tissues were collected at 0, 6, and 12 hr post-UV for analysis with TUNEL assays. TUNEL-positive cells are green and nuclei are stained blue with DAPI. E, epidermis; D, dermis. (B) TUNEL-positive (apoptotic) cells in wild-type and Cry1/2−/− mouse epidermis as a result of UVR at ZT21 (4AM) and ZT09 (4PM). Positive cells were calculated as the percentage of the total number of DAPI-positive cells. All of the values were then normalized to 100 relative to the 12 hr, AM wild-type response sample (which actually had a value of 20% TUNEL-positive cells). (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of TUNEL assay from wild-type and Per1/2−/− mouse skin. Samples were processed as described in B. (D) Quantification of C. AM wild-type response sample contained 10% TUNEL-positive cells but was normalized to 100 for quantification. n=2 or 3 mice at each time point. Error bars represent means ± standard deviation (SD). NS= Not Significant.