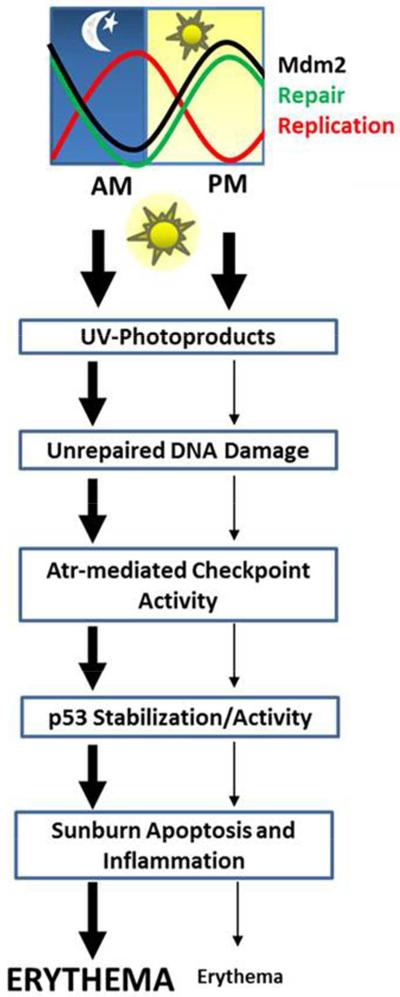
Figure 5.
Proposed model for the role of the circadian clock in sunburn inflammation. Low levels of repair and high levels of DNA replication in the AM lead to unrepaired UV photoproducts in DNA that cause replication stress and to enhanced DNA damage checkpoint signaling compared to in the PM. The enhanced Atr-mediated checkpoint signaling in the AM coupled with reduced levels of Mdm2 lead to greater phosphorylation, stabilization, and activity of p53, which leads to more apoptosis and sunburn following UV exposure in the AM.