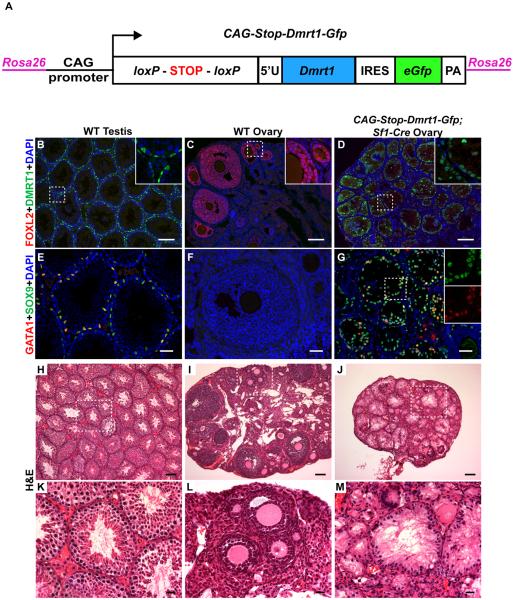
Figure 1. Ectopic DMRT1 in the ovary causes granulosa cell to Sertoli-like cell differentiation.
(A) Schematic diagram of conditional DMRT1 expression transgene CAG-Stop-Dmrt1-Gfp, which is transcribed to express DMRT1 and GFP upon Cre-mediated deletion of a floxed “STOP” cassette (for additional detail see Figure S1A). (B-D) Immunofluorescence (IF) of gonads from 8-10 week old mice showing that activation of CAG-Dmrt1-Gfp in somatic cells of the fetal ovary by Sf1-Cre activates DMRT1, silencing the ovarian granulosa cell transcription factor FOXL2. Dashed boxes indicate areas shown in higher magnification insets. (E-G) IF of adult gonads showing that activation of CAG-Dmrt1-Gfp also activates the Sertoli cell determinant SOX9 and the Sertoli cell differentiation factor GATA1. Dashed boxes indicate areas shown in higher magnification insets. (H-M) Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained sections of adult testes, ovaries, and CAG-Dmrt1-Gfp expressing ovaries, at low and high magnification (dashed boxes indicate magnified areas shown in K-M). Ovaries expressing DMRT1 show tubule-like morphology typical of testes, with polarized Sertoli-like cells lining the periphery and extending cytoplasmic veils into a central lumen. Scale bars: 100 μm (B-D, H-J); 40 μm (E-G); 20 μm (K-M). See also Figure S1.