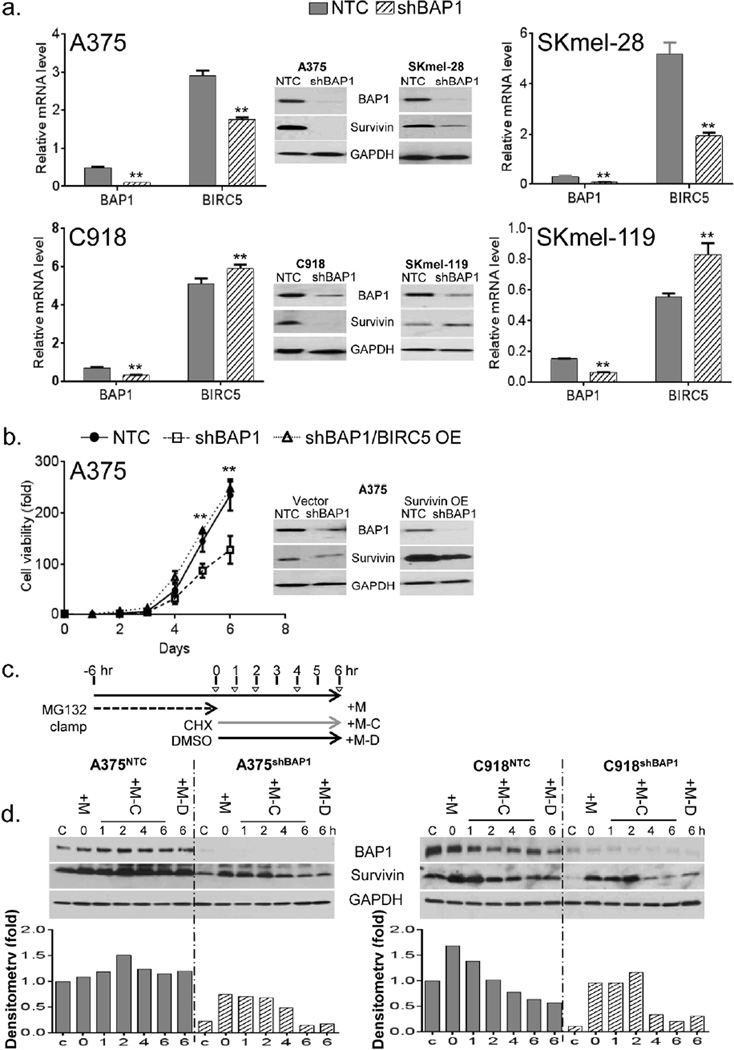
Figure 4. BAP1 suppression is associated with survivin depletion.
(a) RNA and protein levels of BIRC5 (survivin) upon BAP1 suppression in 4 melanoma lines. There is evidence of near total survivin loss at the protein level in A375, SKmel-28 and C918 but not SKmel-119. Error bars represent SEM from triplicate samples; *p<0.05 **p<0.01 by student T test. (b) Survivin over-expression (OE) in A375 cells led to the rescue of the in vitro growth arrest induced by shBAP1. (c) Schematic diagram of experimental design for ubiquitination assay. Indicated cell lines were incubated with MG132 (25 QM) for 6 hours, followed by removal of MG132 and the addition of cycloheximide (CHX, 25 Qg/ml) for the designated time intervals. “C” represents control cells that were exposed to neither MG132 nor CHX. “+M” indicates cells that were exposed to only MG132 and not CHX; for these cells, lysate was collected at time=0. “+M-C” represents cells that were exposed to MG132 and then switched to CHX; lysates were collected at 1, 2, 4 and 6 hrs post-CHX switch. “+M-D” represent cells that were exposed to MG132 and then DMSO control for 6 hours. (d) The effect of BAP1 depletion on survivin and GAPDH protein levels as measured by western blotting. If BAP1 directly deubiquitinated survivin, then survivin decay should be accelerated with BAP1 depletion. Even though the absolute levels of BAP1 appear to be lower in the shBAP1 lines, survivin degradation appears similar. Error bars represent SEM of triplicate samples. The experiments were performed 3 times with similar results; **p<0.01 by student T test.