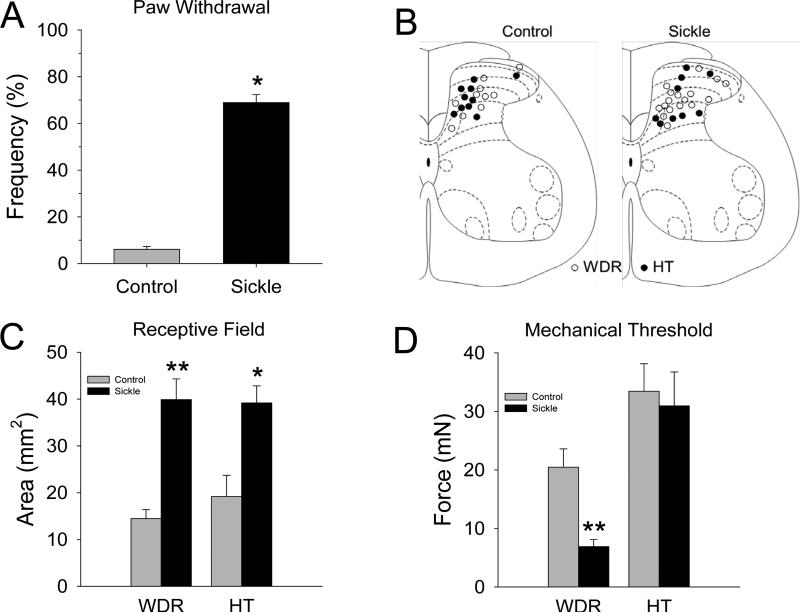
Figure 1.
A) Sickle mice exhibited mechanical hyperalgesia. None of the control mice (n=14) exhibited a withdrawal response frequency greater than 15% (range: 0 to 15%) to this force, whereas sickle mice (n=14) had response frequencies that ranged between 50-100%. The mean (±SEM) frequency of paw withdrawal differed between the groups (t-test, p<0.001). B) Schematic representation of the location of recording sites in the spinal dorsal horn. The location of recording sites for WDR and HT neurons were similar for control (left) and sickle (right) mice and were located throughout the dorsal horn. The mean (±SEM) depths of recording sites from the surface of the spinal cord did not differ between control and sickle mice (307.1 ±32.6 μm and 399.1 ±33.3 μm, respectively). C) The mechano-sensitive receptive field areas of dorsal horn neurons differed between control and sickle mice. Receptive field areas were larger for both WDR and HT neurons in sickle mice (t-tests; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). D) Mechanical thresholds of WDR neurons were lower in mice with SCD as compared to controls (t-tests; **P < 0.01).