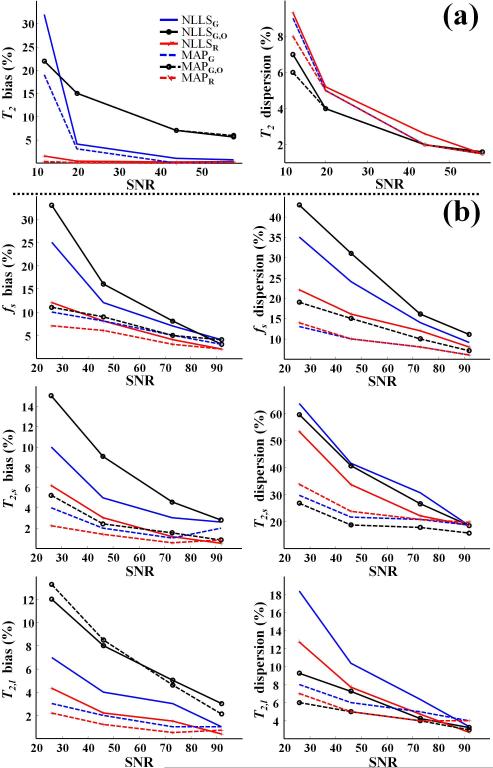
Fig. 6.
Phantom study results showing relative bias and dispersion in parameter estimates as a function of SNR using the fitting methods NLLSG, NLLSG,O, NLLSR, MAPG, MAPG,O and MAPR. (a) Results for T2, assuming the monoexponential signal model with T2 = 58 ms as the underlying parameter value. (b) Results for fs, T2,s and T2,l assuming the biexponential signal model with fs = 0.33, T2,s = 14 ms and T2,l = 112 ms as underlying parameter values. Overall, accuracy and precision were substantially improved through use of Rician noise model and Bayesian analysis; see text for detailed discussion.