Abstract
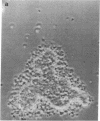
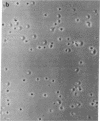
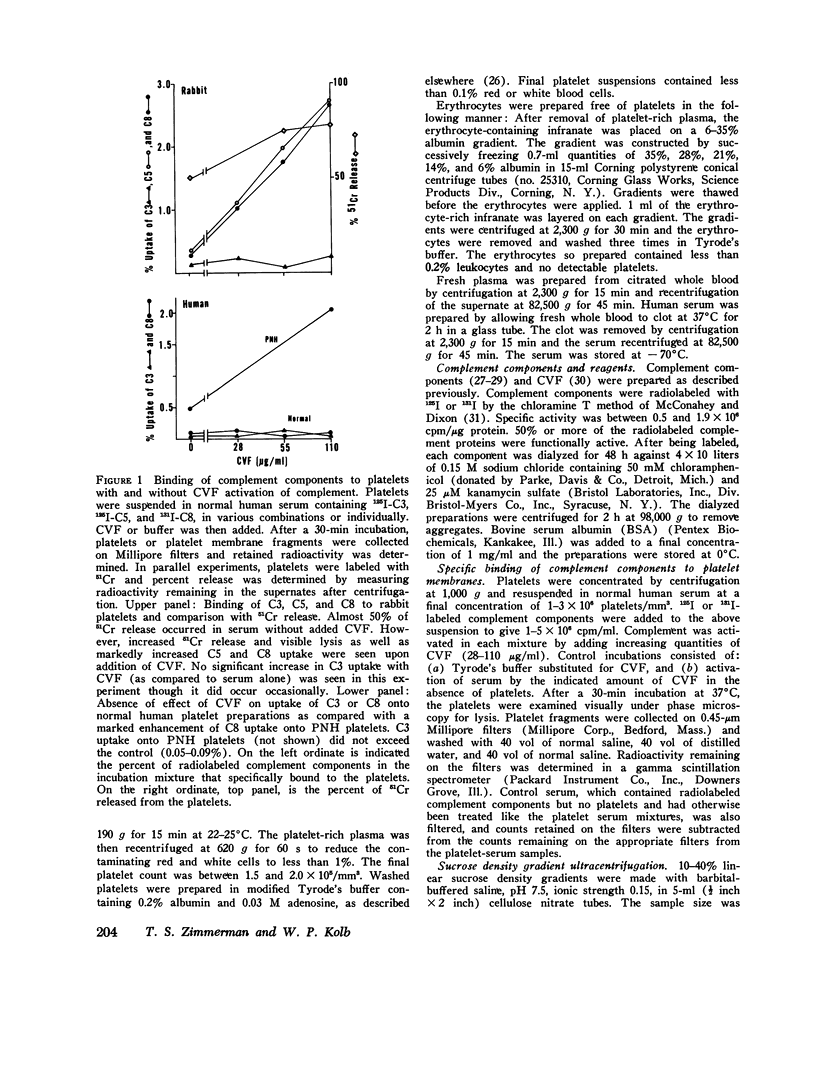
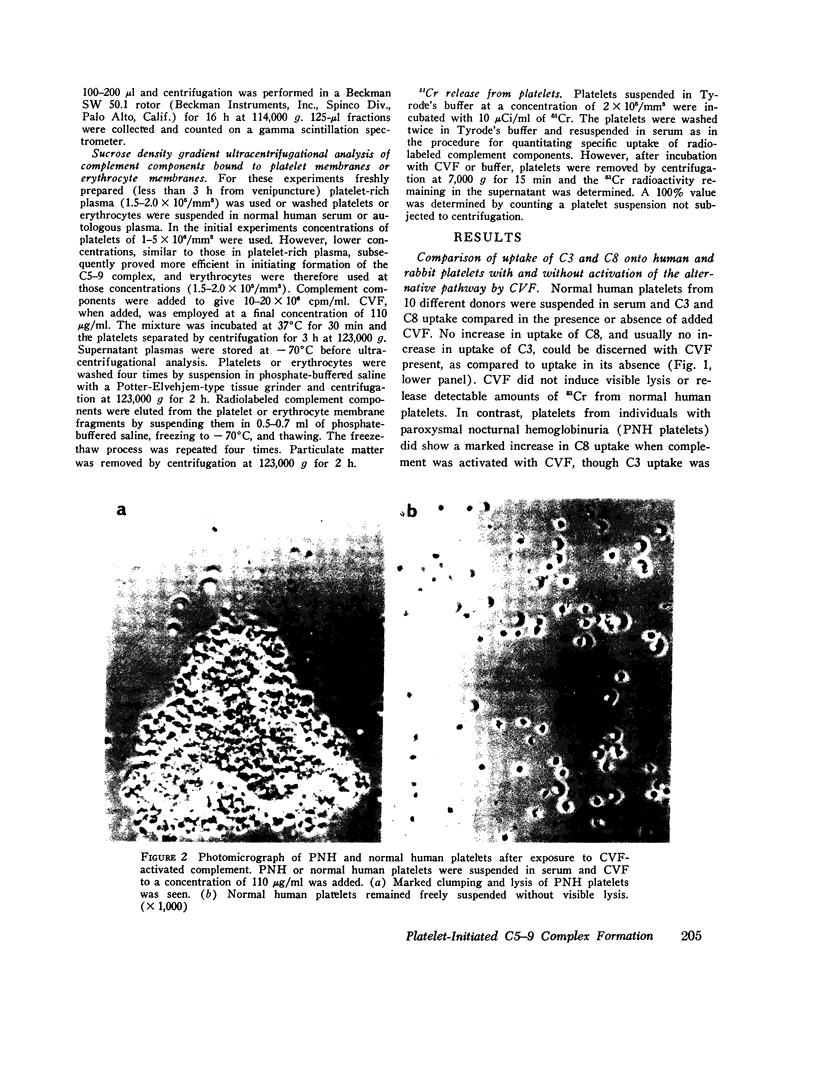
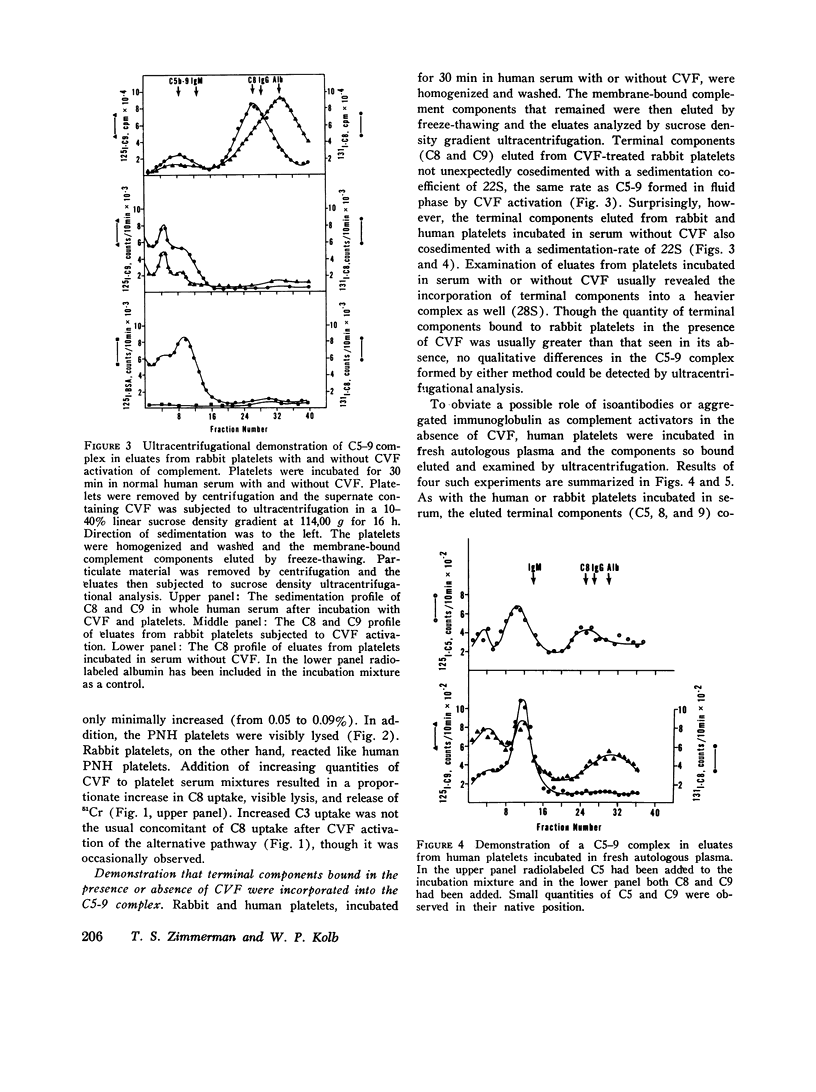
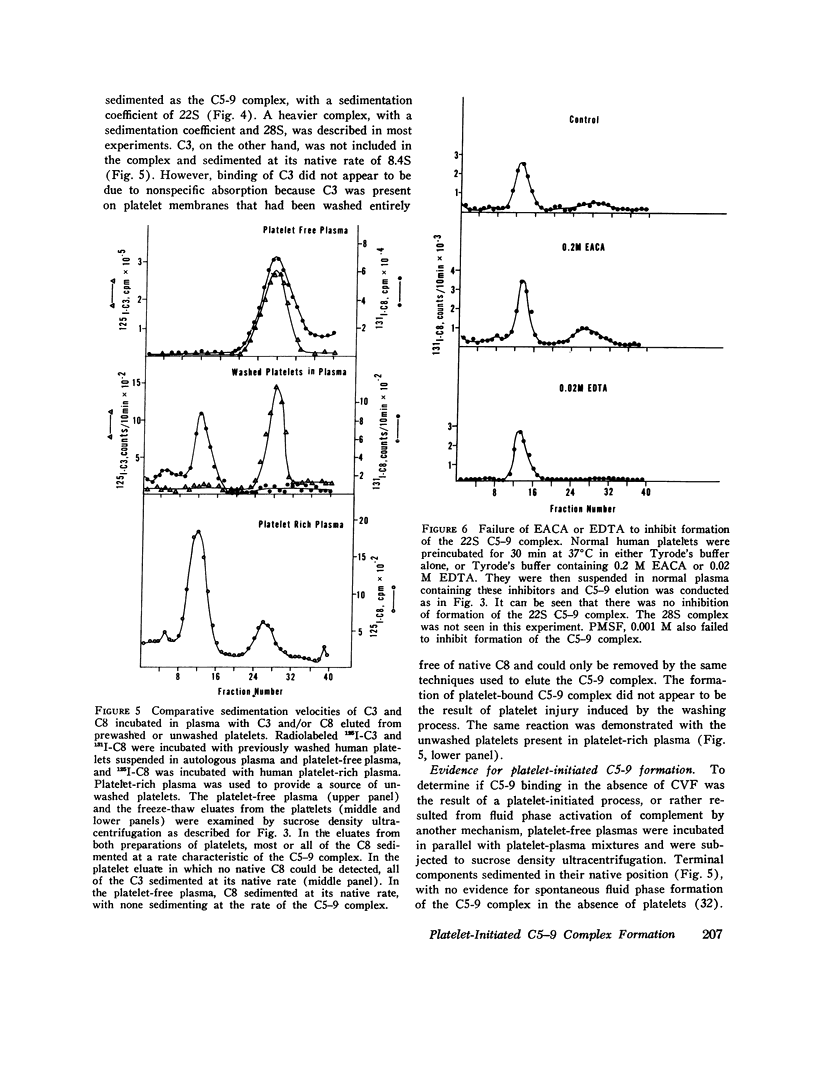
We have studied the interaction of radiolabeled complement components with normal human platelets, platelets from a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, and rabbit platelets in the absence of known complement activators or in the presence of cobra venom factor (CVF). When unwashed platelets in platelet-rich plasma, or washed platelets suspended in serum or autologous plasma, were incubated for 30 min, C3 and terminal components (C5, C8, and C9) were found to bind to them. The terminal components were shown to be bound as the C5-9 complex, rather than as individual proteins, by eluting them from the platelet membrane and examining their behavior on ultracentrifugation. They cosedimented at a rate characteristic of the stable C5-9 complex (22S). As many as 370-1,380 C5-9 complexes/platelet were calculated to have been bound during the incubation period. The complex so formed did not differ by ultracentrifugational criteria from that binding to rabbit platelets after CVF activation of complement. Though C3 was not included in the complex, it did not appear to be bound by nonspecific absorption. It could not be removed by washing but rather was eluted by the freeze-thaw technique used to elute the C5-9 complex. Incubation of radiolabeled components in platelet-free plasma did not result in C5-9 complex formation, indicating an initiating role for platelets in this reaction. In contrast to platelets, erythrocytes incubated in analogous plasma did not induce detectable C5-9 formation. Neither EDTA, phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride, nor epsilon-amino-N-caproic acid prevented platelet-initiated formation of C5-9, suggesting that the reaction may involve mechanisms of complement activation not previously described.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP T. The haemostatic balance. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 Sep 1;2(3-4):347–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aster R. H., Enright S. E. A platelet and granulocyte membrane defect in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: usefulness for the detection of platelet antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1199–1210. doi: 10.1172/JCI106084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. T., Gall E. P., Norman M. E., Nilsson U. R., Zimmerman T. S. Hereditary deficiency of the seventh component of complement. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):905–913. doi: 10.1172/JCI108170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. L., Lachmann P. J. The behaviour of complement and platelets in lethal endotoxin shock in rabbits. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;45(1):193–205. doi: 10.1159/000231028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBY W. H. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: relation of the clinical manifestations to underlying pathogenic mechanisms. Blood. 1953 Sep;8(9):769–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Prez R. M., Bryant R. E. Two mechanisms of immunologically-induced injury to rabbit platelets. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):241–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Prez R. M. The effects of bacterial endotoxin on rabbit platelets. V. Heat labile plasma factor requirements of endotoxin-induced platelet injury. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):966–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds W. J., Pickering R. J. Purified cobra venom factor: effect on blood platelets. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jun;140(2):429–434. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOCKE D. J. IN VITRO DAMAGE OF RABBIT PLATELETS BY AN UNRELATED ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY REACTION. II. STUDIES OF THE PLASMA REQUIREMENT. J Immunol. 1965 Feb;94:247–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Lysis of erythrocytes by complement in the absence of antibody. J Exp Med. 1970 Nov;132(5):898–915. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.5.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWITZ H. I., DES PREZ R. M., HOOK E. W. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on rabbit platelets. II. Enhancement of platelet factor 3 activity in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:619–633. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadding U., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The ninth component of human complement: isolation, description and mode of action. Immunology. 1969 Jun;16(6):719–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Mechanisms of release of constituents from rabbit platelets by antigen-antibody complexes and complement. II. Interaction of platelets with neutrophils. J Immunol. 1970 Aug;105(2):490–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusinkveld R. S., Leddy J. P., Klemperer M. R., Breckenridge R. T. Hereditary deficiency of the sixth component of complement in man. II. Studies of hemostasis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):554–558. doi: 10.1172/JCI107589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalowski S., Howes E. L., Jr, Margaretten W., McKay D. G. Effects of intravascular clotting on the activation of the complement system: The role of the platelet. Am J Pathol. 1975 Mar;78(3):525–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular analysis of the membrane attack mechanism of complement. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):549–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mode of action of human C9: adsorption of multiple C9 molecules to cell-bound C8. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):479–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Verification of a stable C5-9 complex in free solution. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):438–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manni J. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The eighth component of human complement (C8): isolation, characterization, and hemolytic efficiency. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1145–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marney S. R., Jr, Colley D. G., Des Prez R. M. Alternate complement pathway induction of aggregation and release of 5-hydroxytryptamine and adenosine diphosphate by rabbit platelets. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):696–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Fjellström K. E. Isolation of the anticomplementary protein from cobra venom and its mode of action on C3. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON U. R., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. ISOLATION OF BETA IF-GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION AS THE FIFTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:277–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr, Spanondis K., Wilner G. D., Qureshi G. D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):43–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne P. R., Holt J. M., Neame P. B. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria parturition complicated by presumed hepatic vein thrombosis. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1968 Oct;75(10):1066–1068. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1968.tb02884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfueller S. L., Lüscher E. F. Studies of the mechanisms of the human platelet release reaction induced by immunologic stimuli. I. Complement-dependent and complement-independent reactions. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1201–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfueller S. L., Lüscher E. F. Studies of the mechanisms of the human platelet release reaction induced by immunologic stimuli. II. The effects of zymosan. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1211–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P. Platelet requirement in the interaction of the complement and clotting systems. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 18;239(94):208–210. doi: 10.1038/newbio239208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P., Sandberg A. L., Alexander A., Osler A. G. Platelet injury due to activation of the alternate complement pathway. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):490–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielvogel A. R. An ultrastructural study of the mechanisms of platelet-endotoxin interaction. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):235–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomar R. H., Kolchins D. Complement and coagulation. Serum beta-lc-beta-la in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Jul 31;27(3):389–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Coupal C. E. Platelet-dependent generation of chemotactic activity in serum. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1419–1430. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Arroyove C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A blood coagulation abnormality in rabbits deficient in the sixth component of complement (C6) and its correction by purified C6. J Exp Med. 1971 Dec 1;134(6):1591–1600. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.6.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Spiegelberg H. L. Pneumococcus-induced serotonin release from human platelets. Identification of the participating plasma/serum factor as immunoglobulin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):828–834. doi: 10.1172/JCI108161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Grant R. A. Aggregation and release reaction induced in human blood platelets by zymosan. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1219–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Grant R. A., Alper C. A., Goodkofsky I., Lepow I. H. Requirement for complement components and fibrinogen in the zymosan-induced release reaction of human blood platelets. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1744–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]