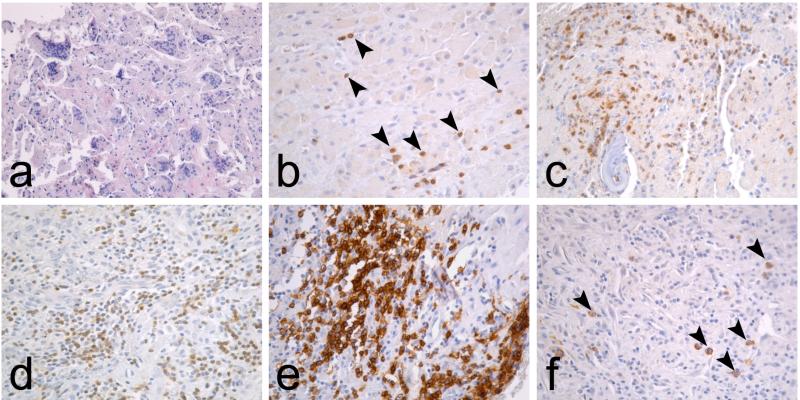
FIG. 1.
Typical interface tissue histopathology in aseptic and septic loosening. (a) Interface tissue developing around aseptically loose TJRs is characterized with macrophage infiltrates and foreign body giant cells. (b) Occasional T lymphocytes (arrowheads), identified by CD3 immunostaining, are scattered among macrophages but neutrophils and other lymphocyte subpopulations are absent. In contrast, the septic interface is characterized by (c) NE+ neutrophil infiltrates, (d) diffuse CD3+ T lymphocyte infiltrates, (e) nodular CD20+ B lymphocyte infiltrates, and (f) occasional CD138+ plasma cells (arrowheads).