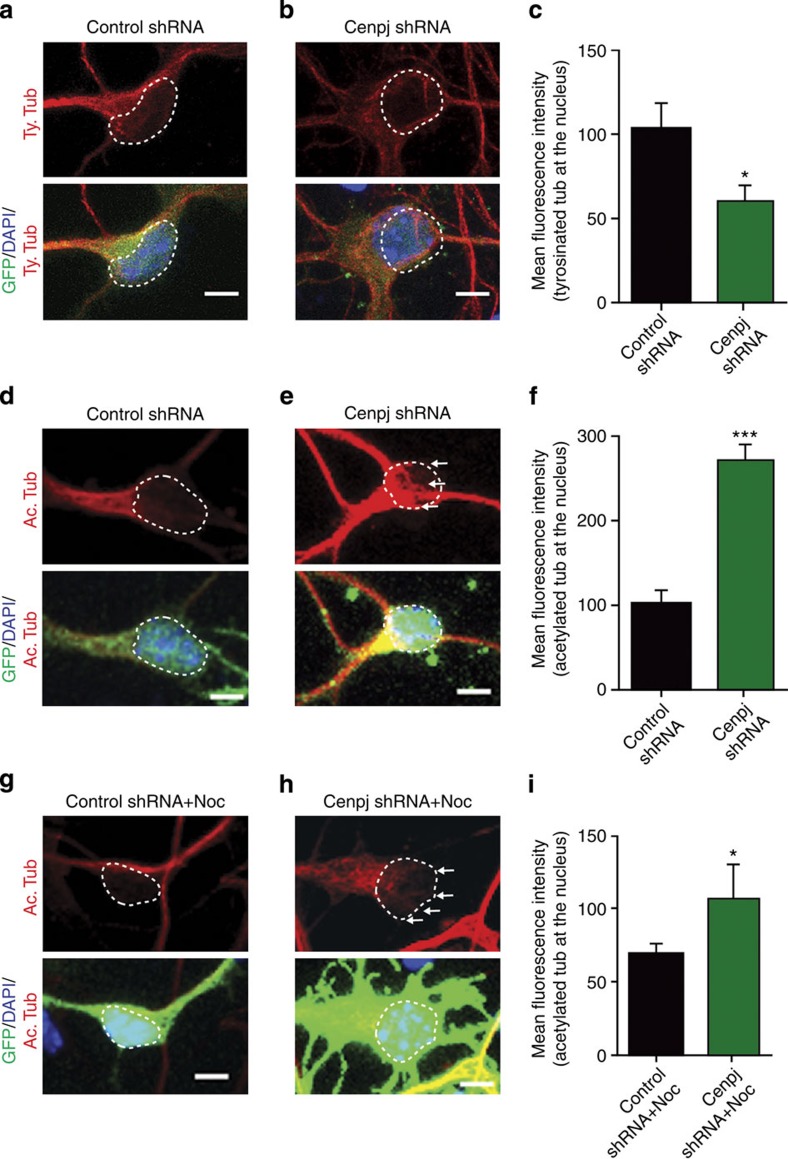
Figure 4. Cenpj silencing disrupts microtubule dynamics.
(a,b,d,e) Analysis of dynamic tyrosinated microtubules (a,b) and stable acetylated microtubules (d,e) in neurons cultured in vitro for 3 days after ex vivo electroporation of GFP and control (a,d) or Cenpj shRNAs (b,e). White line shows 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) limits. Scale bar, 3 μm. (c,f) Quantification of the mean fluorescence intensity of tyrosinated tubulin (c) and acetylated tubulin (f) overlapping the nucleus labelled with DAPI. Cenpj silencing results in a reduction of dynamic microtubules and an increase in stable microtubules in the microtubule cage enveloping the nucleus. The analysis was performed in three independent cultures; control shRNA, n=44 cells; Cenpj shRNA, n=70 (e), control shRNA, n=60 cells; Cenpj shRNA, n=55 (f). Student’s t-test *P<0.05; ***P<0.001. (g,h) Effect of nocodazole on stable acetylated microtubules in neurons cultured in vitro for 3 days after ex vivo electroporation of GFP and control or Cenpj shRNAs (g,h). White line shows DAPI limits. Scale bar, 3 μm. (i) Quantification of acetylated tubulin labelling co-localized with the nucleus in nocodazole-treated cultures. Cenpj silencing results in an increase of stable microtubules in the microtubule cage compared with shRNA control-treated cells (arrows). Analysis of three independent cultures; control shRNA, n=40 cells; Cenpj shRNA, n=42. Student’s t-test *P<0.05.