Figure 2.
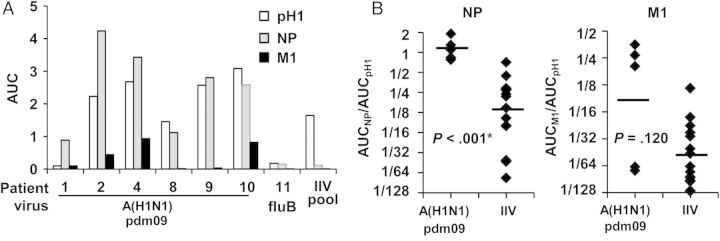
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) plasmablast-derived polyclonal antibody (PPAb) binding to individual influenza virus proteins. A, Six 2009 pandemic influenza A(H1N1) virus (A[H1N1]pdm09)–infected patient PPAb samples with detectable binding to A(H1N1)pdm09 virus, PPAb sample from a patient infected with influenza B virus (fluB), and PPAb pool from inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) recipients (IIV pool) were tested for IgG binding activity to the hemagglutinin (HA) protein of A(H1N1)pdm09 (pH1) and to the nucleoprotein (NP) and matrix 1 protein (M1) of influenza A(H1N1). B, IgG binding activity for NP and M1 were normalized to that for HA by calculating the area under the curve (AUC) ratios (ie, AUCNP/AUCHA and AUCM1/AUCHA) for each PPAb sample. Normalized data from infected patients and the IIV recipients are compared. The A(H1N1)pdm09-infected patient PPAbs with detectable binding to HA (n = 5) and PPAbs from a group of 15 randomly selected 2010/2011 IIV recipients were used for this analysis. The selection of this group was not based on any biological parameters. Horizontal bars indicate the geometric mean of the AUC ratio. The P values were determined by unpaired t tests and adjusted by sequential Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons. The asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference after the adjustment.
