Figure 3.
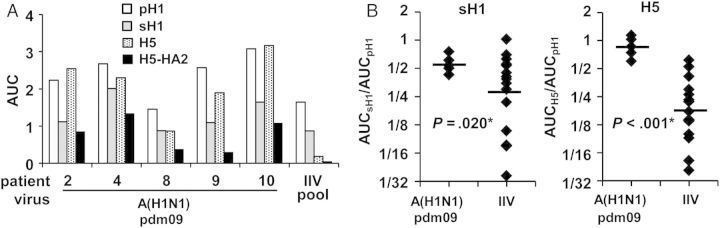
Cross-reactive plasmablast-derived polyclonal antibody (PPAb) binding activity to influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA). A, The 2009 pandemic influenza A(H1N1) virus (A[H1N1]pdm09)–infected patient PPAb samples with detectable binding to the homologous HA of A(H1N1)pdm09 (pH1; n = 5) and the inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) PPAb pool were tested for immunoglobulin G (IgG) binding to the HA of the heterovariant H1N1 strain A/Brisbane/59/2007 (sH1), the heterosubtypic avian H5N1 strain A/Vietnam/1203/2004 (H5), and the HA2 domain of H5 (H5-HA2). B, IgG binding activity for sH1 and H5 were normalized to that for pH1. The A(H1N1)pdm09-infected patient PPAbs with detectable binding to pH1 (n = 5) and PPAbs from the 15 randomly selected individual IIV recipients were included for this analysis. Horizontal bars indicate geometric mean of the area under the curve (AUC) ratio. The P values were determined by unpaired t tests and adjusted by sequential Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons. The asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference after the adjustment.
