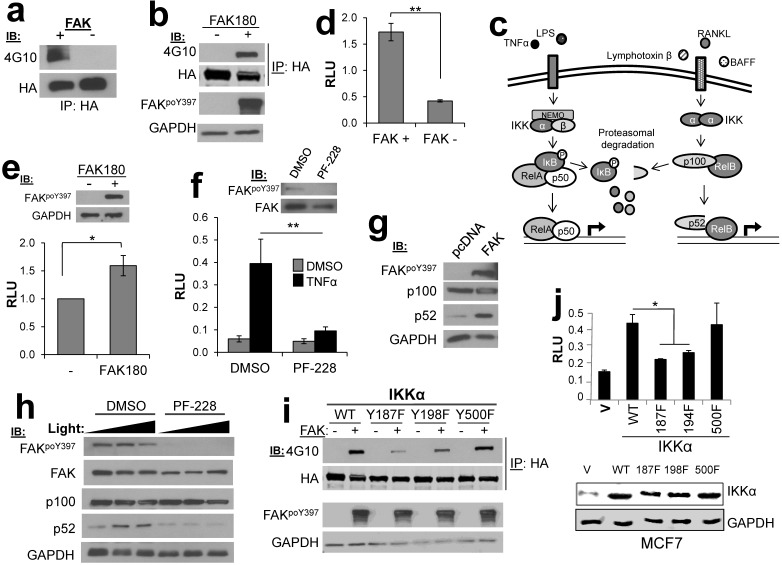
Figure 4.
FAK phosphorylates CHUK/IKKα regulates NFκB signaling. a. FAK-IVK reaction using HA-IKKα IPs, identified by anti-PTyr IB. b. FAK180 phosphorylation of HA-IKKα in HEK293T cells. c. IKKα functions in both canonical (left side) and non-canonical (right side) NFκB pathways. d. Relative luciferase units (RLU) of NK-Luciferase reporter (normalized to CMV-Renilla) in FAK +/+ vs. FAK-/- MEF. e. RLU (NK-Luc vs CMV-Renilla) in FAK-/- cells transiently overexpressing FAK180. f. RLU (NK-Luc vs CMV-Renilla) in MCF7 cells stimulated with TNFα (20ng/mL for 16 h). IB for active and total FAK (upper panel). g. FAK induces cleavage of p100 to p52 in HEK293T cells. h. p100 to p52 cleavage in HeLa cells ectopically expressing p100, after stimulation with 100 or 200 ng/mL Light for 16 h in the presence of either DMSO or 10 μM PF-228. i. Decreased FAK180-induced pTyr of IKKα187F and IKKα198F relative to WT or IKKα500F in HEK293T cells ("-", vector). j. Decreased RLU (NK-Luc vs CMV-Renilla) in MCF7 transiently expressing IKKα187F and IKKα198F relative to WT or IKKα500F (V, vector). Error bars for all experiments: SEM, three independent experiments. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.005 as determined by unpaired t test.