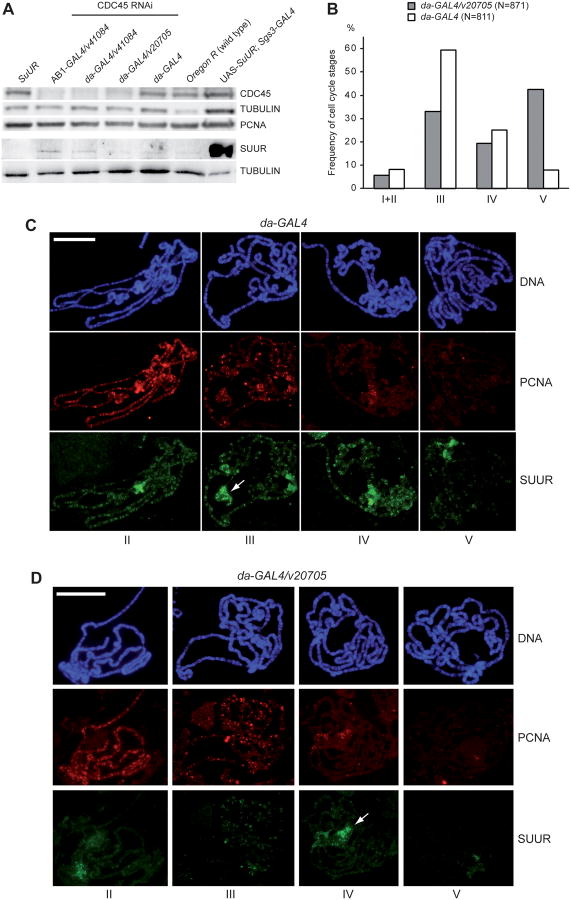
Figure 2.
CDC45 depletion suppresses the endo cycle and inhibits SUUR binding to polytene chromosomes.
(A) Western blot analysis of salivary glands of different genetic backgrounds with anti-CDC45, anti-PCNA, anti-SUUR. TUBULIN was used as a loading control.
(B) Frequencies (%) of salivary gland nuclei at different S-phase stages. Endo cycle stages were determined according to (Kolesnikova et al., 2013): (I-II) the early S-phase and early to late S-phase transition; (III) “typical” late S-phase; (IV) the end of S-phase; and (V) G-phase.
(C, D) Salivary gland polytene chromosomes were co-immunostained with SUUR (green) and PCNA (red), DNA was detected by DAPI. da-GAL4 control (C) and da-GAL4/cdc45-RNAi-v20705 (D). SUUR signal intensity was significantly reduced upon CDC45 depletion; N=871 for da-GAL4/cdc45-RNAi-v20705 and N=811 for the da-GAL4 control. Arrows indicate SUUR binding to the nucleolus. Scale bar = 50 μm.