| a |
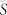 = 3,000, τ = 1 = 3,000, τ = 1 |
Original EW model |
| |
|
Strong selection |
| |
|
Absolute trait effect and fitness effect linearly correlated |
| b |
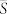 = 30, τ = 1 = 30, τ = 1 |
Original EW model |
| |
|
Weak selection |
| |
|
Absolute trait effect and fitness effect linearly correlated |
| c |
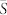 = 3,000, τ = 0 = 3,000, τ = 0 |
Original EW model |
| |
|
Strong selection |
| |
|
Absolute trait effect and fitness effect uncorrelated |
| d |
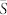 = 3,000, τ = 0.5 = 3,000, τ = 0.5 |
Original EW model |
| |
|
Strong selection |
| |
|
Absolute trait effect and fitness effect weakly correlated |
| e |
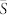 = 3,000, τ = 2 = 3,000, τ = 2 |
Original EW model |
| |
|
Strong selection |
| |
|
Quadratic relationship between absolute trait effect and fitness effect |
| f |
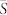 = 3,000,A = 10,000,B = 10,000 = 3,000,A = 10,000,B = 10,000 |
Saturating function |
| |
|
Strong selection |
| |
|
Absolute trait effect threshold of 10,000 before noise term (1 + ε) |
| |
|
Linear relationship between trait and fitness near origin with gradient 1 before noise term δ(1 + ε) |
| g |
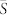 = 3,000,A = 4,000,B = 40 = 3,000,A = 4,000,B = 40 |
Saturating function |
| |
|
Strong selection |
| |
|
Absolute trait effect threshold of 4,000 before noise term (1 + ε) |
| |
|
Linear relationship between trait and fitness near origin with gradient 100 before noise term δ(1 + ε) |
| h |
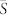 = 3,000,A = 4,000,B = 4,000 = 3,000,A = 4,000,B = 4,000 |
Saturating function |
| |
|
Strong selection |
| |
|
Absolute trait effect threshold of 4,000 before noise term (1 + ε) |
| |
|
Linear relationship between trait and fitness near origin with gradient 1 before noise term δ(1 + ε) |
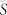 = 3,000, τ = 1
= 3,000, τ = 1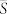 = 30, τ = 1
= 30, τ = 1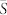 = 3,000, τ = 0
= 3,000, τ = 0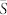 = 3,000, τ = 0.5
= 3,000, τ = 0.5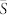 = 3,000, τ = 2
= 3,000, τ = 2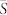 = 3,000,A = 10,000,B = 10,000
= 3,000,A = 10,000,B = 10,000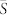 = 3,000,A = 4,000,B = 40
= 3,000,A = 4,000,B = 40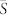 = 3,000,A = 4,000,B = 4,000
= 3,000,A = 4,000,B = 4,000