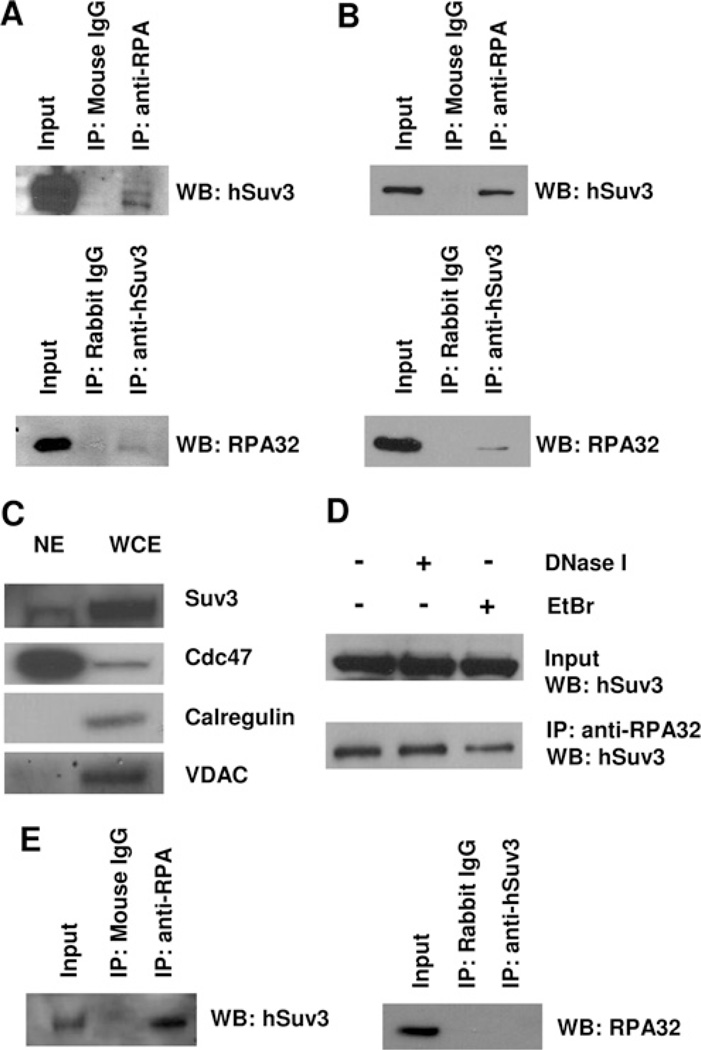
Figure 2. Interaction of RPA with hSuv3.
(A) Interaction of RPA with hSuv3 in HeLa whole cell extract. Total cell lysates were used for co-IP assays with anti-RPA, anti-hSuv3 or normal IgG antibody. (B) RPA and hSuv3 interact in the nuclear fraction. HeLa nuclear extracts (1 mg) were used for co-IP as in (A). (C) Western blot analysis (WB) of nuclear extract (NE). The nuclear extract used in (B) and whole cell extract (WCE) were analysed for the presence of subcellular markers calregulin (cytoplasm), VDAC (mitochondria) and Cdc47 (nucleus). (D) The hSuv3–RPA interaction is independent of DNA. HeLa nuclear extracts (1 mg) were either untreated or treated with 0.2 unit/(µg of protein) DNase I for 20 min at 37°C or 50 µg/ml EtBr for 30 min on ice, before co-IP as in (A). (E) RPA and hSuv3 interact in the nuclear fraction of GM38 primary human fibroblasts. Nuclear extracts were used for co-IP as in (B).