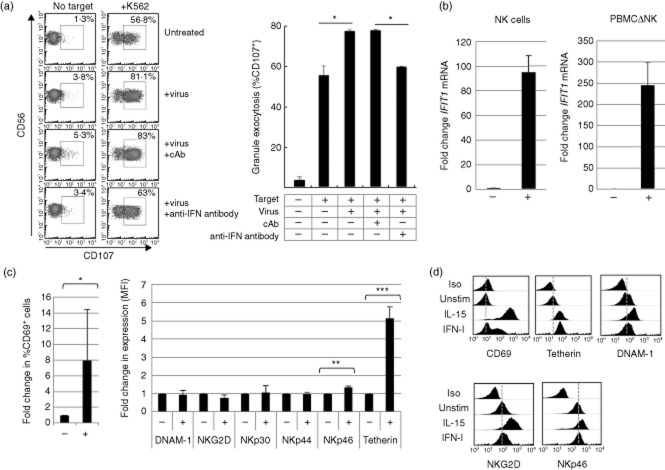
Figure 3.
Analysis of natural killer (NK) cell responses to reovirus treatment in vitro. (a) Reovirus and interferon (IFN)-I-mediated activation of NK cell granule exocytosis. The left-hand panel shows the display of cell surface CD107 (gated on CD56+CD3– NK cells within peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) in the presence or absence of K562 target cells. The experiment was performed using PBMC from healthy donors without further treatment (untreated), in the presence of 0·2 multiplicity of infection (MOI) reovirus (+virus) and in the presence of reovirus and an anti-IFN antibody or a control antibody (cAb). The percentage values indicate the proportion of CD107+ NK cells for each treatment. Statistical analysis was performed between the indicated pairs of treatments using Student's t-test; *P < 0·05. Limitations in the size of samples available from the clinical trial made cytotoxicity assays from the in vivo study difficult to perform. However, of three patients analysed, one showed increased cytotoxic activity 48 h post-infection (data not shown). (b) Expression of IFIT1 mRNA in NK cells and NK cell-depleted PBMC (PBMCΔNK) with (+) and without (–) reovirus treatment in vitro. Whole PBMC (from healthy donors) were treated with reovirus (at an MOI of 1), cultured for 48 h and fractionated into NK cells and NK-depleted PBMC (using magnetic indirect selection of NK cells). Reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR) for IFIT1 and ABL1 was performed using mRNA isolated from these fractions; IFIT1 expression was normalized to ABL1 mRNA and the fold-change induced during infection calculated via the ΔΔCt, with the untreated cells (–) assigned an expression value of 1 unit. The data shown are from two different donors. (c) The expression of NK cell surface markers ± reovirus treatment in vitro, analysed 48 h post-infection. The left-hand panel indicates the percentage of CD69 expressing NK cells in the PBMC population, the right-hand panel indicates the change in mean fluorescence intensity of the indicated markers. Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t-test; *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01; ***P < 0·001. (d) Expression of NK cell surface molecules following cytokine treatment in vitro. Purified NK cells (from healthy donors) were treated with 20 ng/ml of interleukin (IL)-15 or 100 IU interferon (IFN)-I for 48 h and expression of the indicated markers was analysed by flow cytometry. The dotted grey line shows the approximate position of the mean fluorescence intensity of the isotype control for CD69 and, for other markers, their expression in untreated cells.