Figure 1.
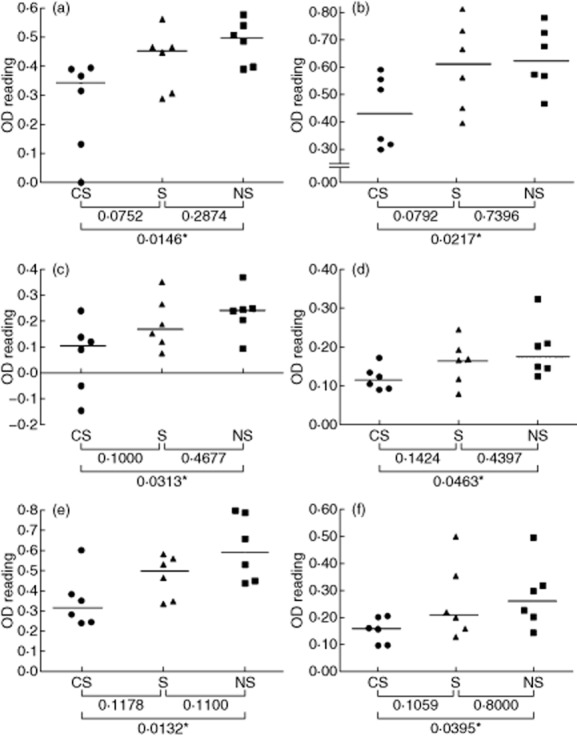
Detecting serum immunoglobulin (Ig)G autoantibodies that bind to constituents of human lung tissue. Sera from smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (CS), smokers (S) and non-smokers (NS) were analysed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for IgG antibodies that bind to human lung tissue homogenates. The sources of the lung tissue were as follows: (a,b) CS patients; (c,d) S subjects; (e,f) NS subjects. Each point represents an individual serum sample, and the horizontal line is the median optical density (OD) value of the group; statistical comparisons between groups were performed using the Mann–Whitney U-test. The lung samples and the sera were obtained from different subjects.
