Figure 3.
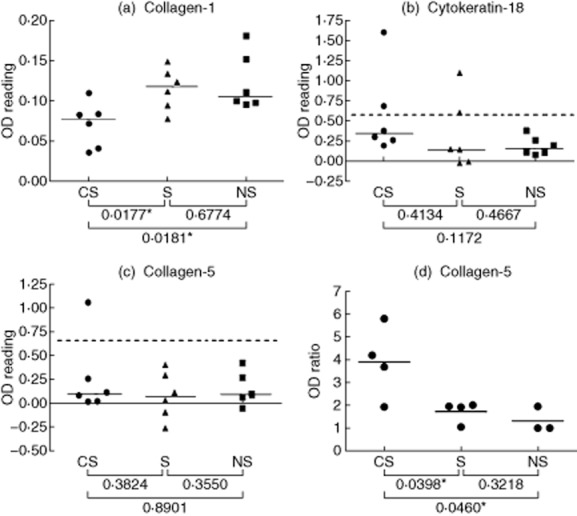
Detecting serum and lung-associated immunoglobulin (Ig)G autoantibodies that bind to candidate lung antigens. (a–c) Sera from smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (CS), smokers (S) and non-smokers (NS) subjects were analysed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for IgG antibodies that bind to pure protein antigens [collagen-1, (a); cytokeratin-18, (b); collagen-5 (c)]. Each point represents an individual serum sample, and the horizontal lines are the median optical density (OD) values of the groups. Statistical comparisons between groups were performed using the Mann–Whitney U-test. Dashed lines represent 1·5 times the upper limit of the range of ODs given by the NS sera. (d) Eluates of lung tissue from CS, S and NS subjects were analysed by ELISA for IgG antibodies that bind to pure protein antigens. Each point represents an individual lung tissue eluate, and the standardized values shown are the ratio of the OD for eluted IgG binding to collagen-5 divided by the OD for the binding of the same eluted IgG to thyroglobulin (negative control antigen); the horizontal bars are the mean standardized values of the groups. Significant differences between groups were tested by Student's t-test.
