Figure 3.
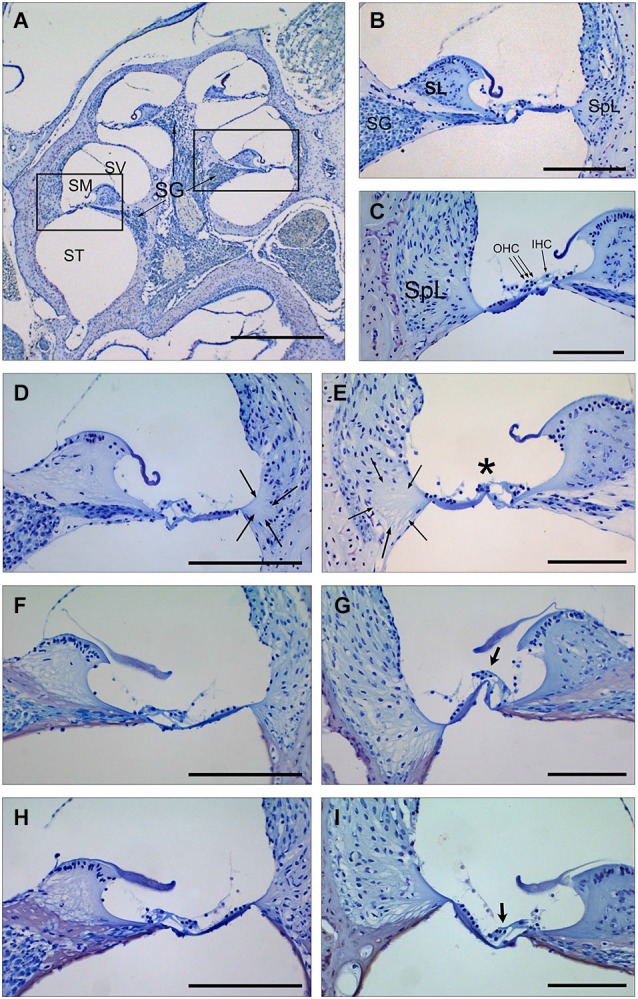
Cochlear morphology in mice treated with TGF-β1 inhibitors before being exposed to noise. (A–C) Midmodiolar section (A) and detail of the scala media from middle (B) and basal (C) turns of the cochlea in a control non-exposed mouse, showing normal cytoarchitecture of spiral limbus (SL), spiral ligament (SpL) and organ of Corti with the outer and inner hair cells (D–I) Details of the spiral limbus, spiral ligament and organ of Corti from a representative MF1 mouse pre-treated with saline (D,E), P17 (F,G) or P144 (H,I) before noise exposure. Mice treated with saline showed loss of fibrocyte cells in the spiral ligament (arrows) in the basal and middle turns of the cochlea and outer hair cells in the organ of Corti (asterisk) in the basal turn. In contrast, mice receiving TGF-β1 inhibitors presented preserved cochlear structures, with the presence of OHC even in the basal turn (arrows in G,I). Scale bars: A, K 0.5 mm; (C–G), 100 μm. SG, spiral ganglion; SV, scala vestibule; SM, scala media; ST, scala tympani; SL, spiral limbus; SpL, spiral ligament; OHC, outer hair cells; IHC, inner hair cells.
