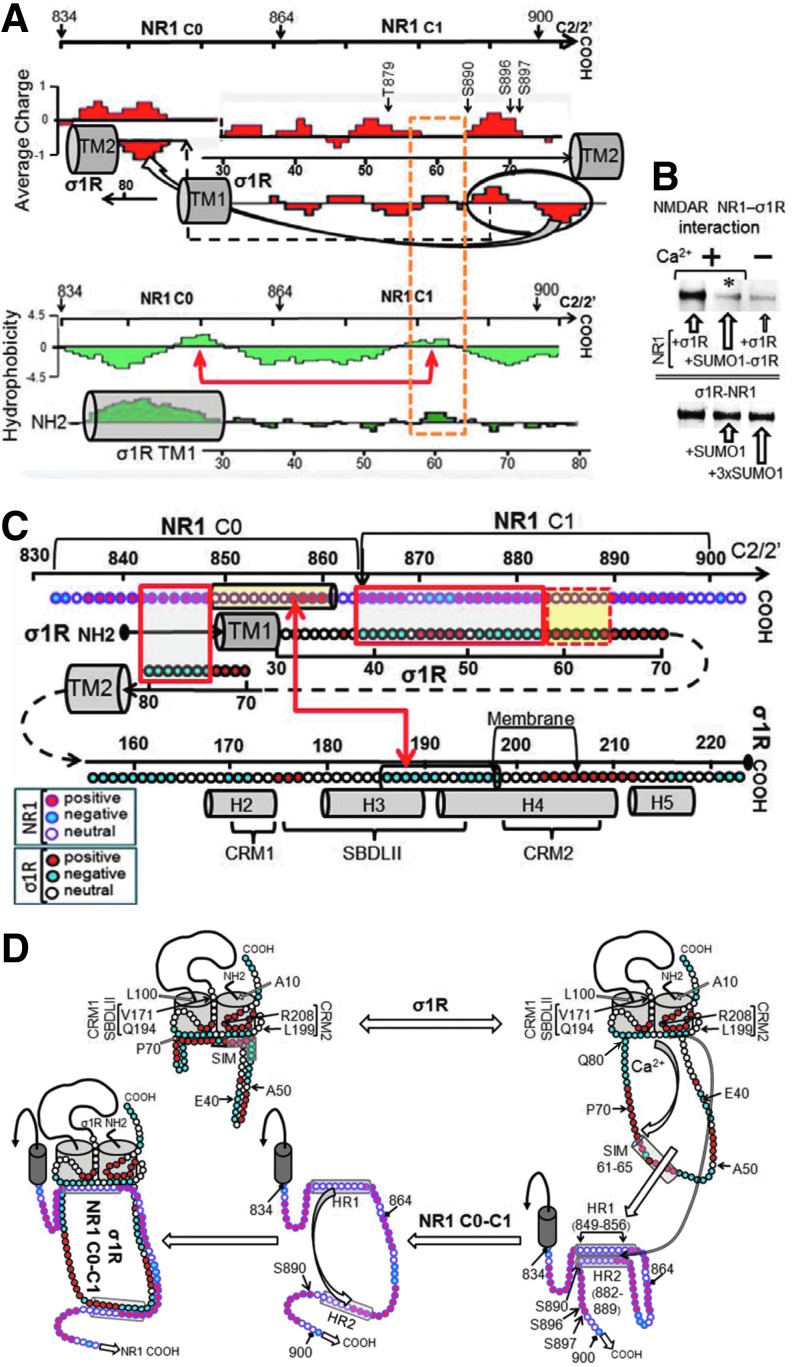
FIG. 3.
Juxtaposition of the σ1R and NR1 C0-C1 regions based on their charge complementarities and hydrophobicity. (A) Proposed interaction of the σ1R loop with the NMDAR NR1 C0-C1 region. The discontinuous yellow frame indicates possible hydrophobic interactions. TM stands for transmembrane region. The arrows on the NR1 sequence suggest a possible intramolecular interaction between the HR1 and HR2 hydrophobic regions (Lasergene Protean V8 DNASTAR). (B) Influence of SUMO1 on the σ1R association with NR1 subunits. The recombinant σ1R protein (100 nM) was preincubated with agarose-SUMO1. After the removal of the free σ1Rs, the NR1 subunits (100 nM) were added to the incubation milieu. In a set of assays, preformed agarose-NR1-σ1R complexes (100 nM) were incubated with free SUMO1. The agarose pellets containing the bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting. (C) Model describing the potential interaction regions of the complete σ1R with NR1 C0-C1 segments. Closed boxes indicate charge complementarities, and open boxes indicate potential hydrophobic interaction. The arrows connect the HR on NR1 C0 with another region in σ1Rcd corresponding to SBDLII, a negative region that could bind calcium. TM stands for transmembrane domain, and the helix organization (H2–H5) is taken from Ortega-Roldan et al. (43). Key indicates amino acid charge for NR1 and s1R. (D) Diagram of calcium-dependent σ1R binding to the NR1 C terminal C0-C1 region. The σ1R loop in the cell membrane is oriented toward the cytosolic side, and both the N and C terminal sequences face the extracellular space. The hydrophobic cd region is oriented toward the inner side of the membrane and between the TM domains, forming the ligand-binding pocket. This hydrophobic and negative cd region interacts with a positive region of the σ1R loop. The position of certain residues is indicated in the figure. On calcium binding, this negative cd region becomes neutral and subsequently releases the positive loop region to bind other proteins, such as the NR1 subunit. Peptide interference mapping suggests that the NR1 HR1 and HR2 hydrophobic regions establish an intramolecular interaction. The calcium-bound σ1Rcd region would disrupt this internal interaction to bind to the NR1 subunit.