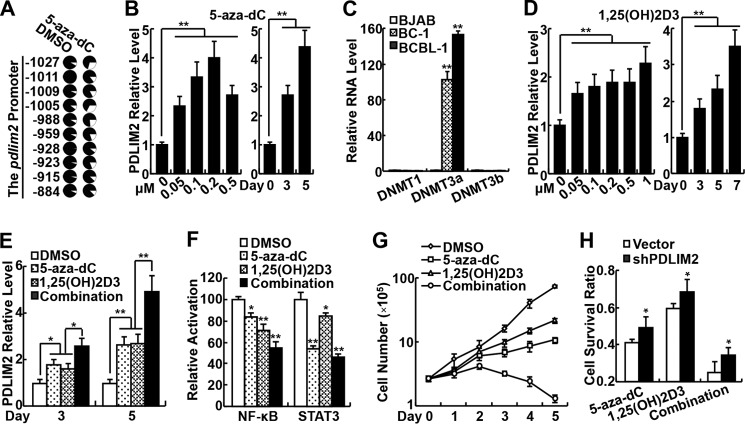
FIGURE 4.
PDLIM2 repression by KSHV involves its promoter methylation and can be reversed by 5-aza-2-dC and vitamin D to inhibit growth of KSHV-associated tumor cells. A, bisulfite genomic DNA sequencing showing epigenetic repression of PDLIM2 in BCBL-1 cells. Each circle represents a CpG site, and the ratio of the filled area in each circle represents the percentile of methylation in the CpG site. The position of each CpG nucleotide relative to the PDLIM2 transcription initiation site (+1) is indicated at the side. 5-aza-dC treatment: 0.2 μm for 4 days. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. B, qPCR analyses showing dose- and time-dependent re-induction of PDLIM2 by 5-aza-dC in BCBL-1 cells. 5-aza-dC treatment: left, 4 days; right, 0.2 μm. C, qPCR analyses showing increased RNA level of DNMT3a, but not DNMT1 or DNMT3b in PEL cells. D, qPCR analyses showing dose- and time-dependent re-induction of PDLIM2 by vitamin D in BCBL-1 cells. 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment: left, 4 days; right, 0.1 μm. E, qPCR analyses showing cooperation of 5-aza-dC and vitamin D in PDLIM2 re-induction in BCBL-1 cells. F, gene reporter assays showing inhibition of transcriptional activity of NF-κB and STAT3 by 5-aza-dC and vitamin D in BCBL-1 cells. G, cell counting assays showing synergistic growth inhibition of BCBL-1 cells by 5-aza-dC and vitamin D. H, cell counting assays showing that growth inhibition of BCBL-1 cells by 5-aza-dC and/or vitamin D (3-day treatment) can be blocked by PDLIM2 knockdown. For E–H, 5-aza-dC, 0.05 μm; 1,25(OH)2D3, 0.1 μm. Data are mean ± S.D. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.