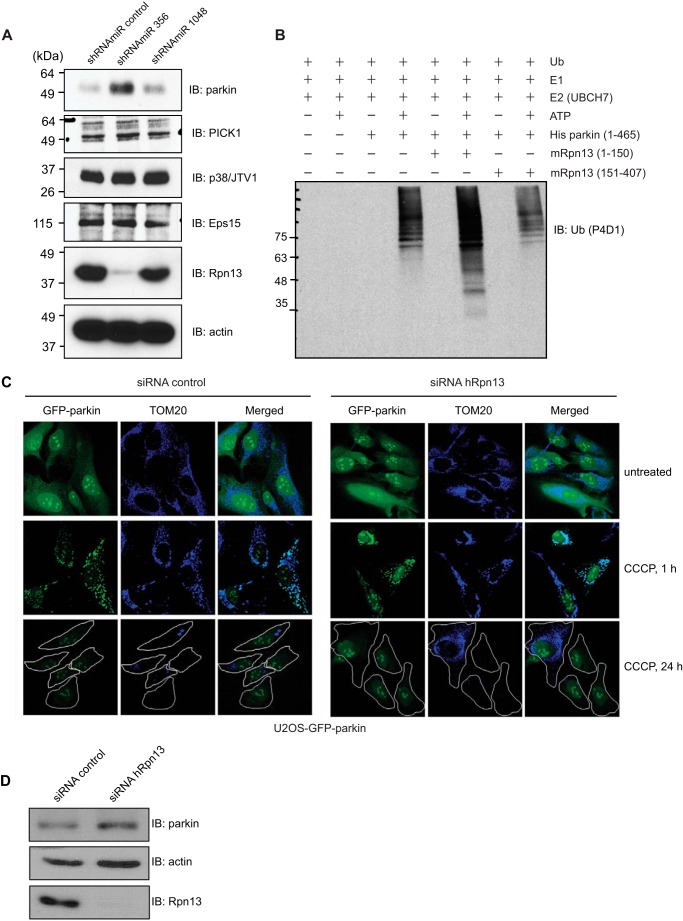
FIGURE 5.
Interaction with Rpn13 increases the E3 ligase activity of parkin, whereas Rpn13 knockdown leads to increased level of parkin protein levels and has no effect on mitochondrial recruitment of parkin. A, parkin levels increase upon knockdown of Rpn13. Parkin protein levels only increase when shRNAmiR 356 and not the knockdown-ineffective shRNAmiR 1048 or control shRNAmiR are used. None of the analyzed parkin substrates (PICK1, p38/JTV1, and Eps15) were affected by the Rpn13 knockdown. Efficiency of Rpn13 silencing in HEK293T cells using lentivirus-delivered shRNAmiR against Rpn13 (shRNAmiR 356 and shRNAmiR 1048) and a control shRNAmiR was assessed by immunoblotting for Rpn13 and actin (as a loading control). B, in vitro ubiquitination reaction with purified His-parkin as E3 ligase. Reaction mixture (E1, E2 UbcH7, ATP, and ubiquitin) was complemented with equal amounts of various fragments of purified Rpn13. C, knockdown of Rpn13 has no effect on the mitochondrial recruitment of parkin or on the autophagic clearance of mitochondria. U2OS-GFP-parkin cells were transfected with nontargeting or Rpn13 siRNA (10 nm) for 60 h. Untreated cells or cells treated with CCCP for 1 or 24 h were fixed, and images were acquired after staining for the mitochondrial protein, TOM20. D, validation of Rpn13 siRNA knockdown. U2OS-GFP-parkin cells were transfected with nontargeting or Rpn13 siRNA oligonucleotides (10 nm) for 60 h. Cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting for Rpn13, parkin, and actin. IB, immunoblotting.