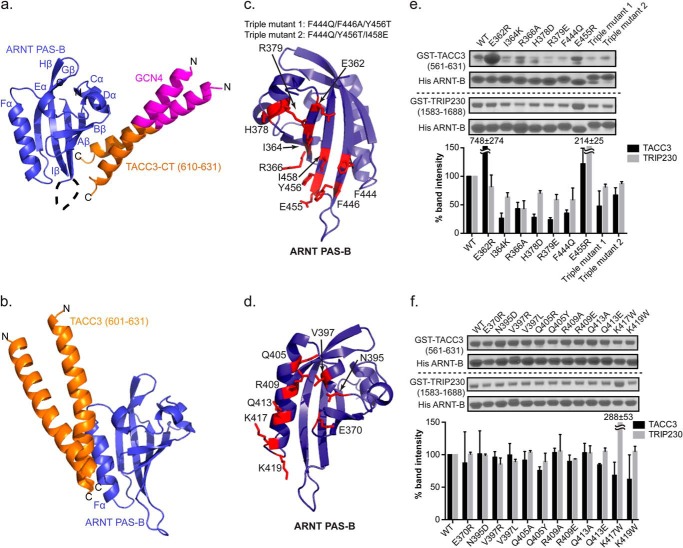
FIGURE 2.
Structure and validation of the ARNT PAS-B·GCN4-TACC3-CT D622A/E629A complex. a, crystal structure of ARNT and TACC3 minimum interacting fragments (PDB code 4LPZ) as follows: ARNT PAS-B (blue)·GCN4-TACC3-CT D622A/E629A (orange). The GCN4 dimerization tag engineered into the TACC3 fragment is shown in magenta. In this structure, TACC3 binds to the β-sheet side of the ARNT PAS-B domain. b, HADDOCK model of a previous ARNT PAS-B·TACC3 complex model, showing TACC3 binding to ARNT PAS-B on the Fα helix (6). c and d, locations of sites on ARNT PAS-B β-sheet (c) and Fα helix (d) to test the structural models of ARNT/TACC3 interactions. e, Ni2+ pulldown assay and band quantification (mean ± one S.D., n = 2) shows that His-ARNT PAS-B β-sheet mutations modulate the binding of WT GST-TACC3, indicating that the β-sheet of ARNT PAS-B is the direct TACC3 binding interface. Similar to TACC3 interaction, nickel pulldown assay and band quantification (mean ± one S.D., n = 2) shows His-ARNT PAS-B β-sheet mutations change its affinity for WT GST-TRIP230(1583–1688), indicating that the β-sheet of ARNT PAS-B is the major interface for TRIP230 binding as well. f, nickel pulldown assay and band quantification show that His-ARNT PAS-B Fα mutation is unable to alter its affinity with WT GST-TACC3(581–631) and WT GST-TRIP230(1583–1688), indicating that the Fα is not the major CCC binding interface.