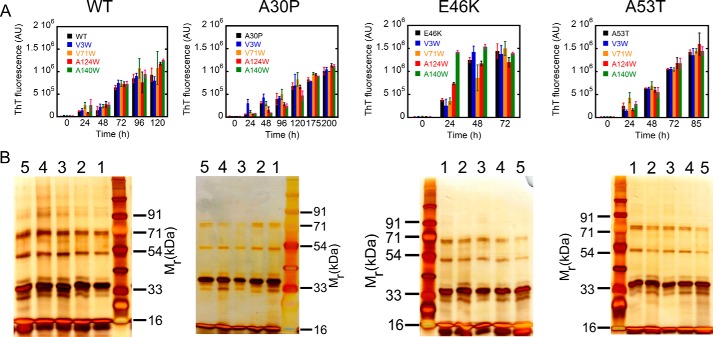
FIGURE 5.
Effect of Trp substitutions on the aggregation propensities and early oligomerization of the respective parent proteins. A, amyloid formation of WT α-Syn and its three PD-associated mutants (E46K, A53T, and A30P) along with their Trp-substituted variants monitored by ThT fluorescence. ThT fluorescence at 480 nm is plotted as a function of time (in h). Mutants E46K and A53T and their Trp-substituted variants have a faster rate of amyloid formation, whereas A30P and its Trp-substituted variants have a slower amyloid forming rate compared with WT α-Syn and its Trp-substituted variants. B, the early oligomerization was studied for α-Syn and its Trp mutants using PICUP followed by SDS-PAGE. A silver-stained gel shows the cross-linked products of the parent protein (lane 1), V3W variant (lane 2), V71W variant (lane 3), A124W variant (lane 4), and A140W variant (lane 5). In all proteins, distinct bands corresponding to monomer (∼17 kDa), dimer (∼33 kDa), trimer (∼54 kDa), and pentamer (∼71 kDa) were observed, indicating that none of the Trp substitutions affect the early oligomer size distributions of their parent proteins. Error bars represent S.D. AU, arbitrary units. In B, SDS-PAGE gels (from left to right) represent proteins samples of WT, A30P, E46K, and A53T α-synuclein.