FIGURE 8.
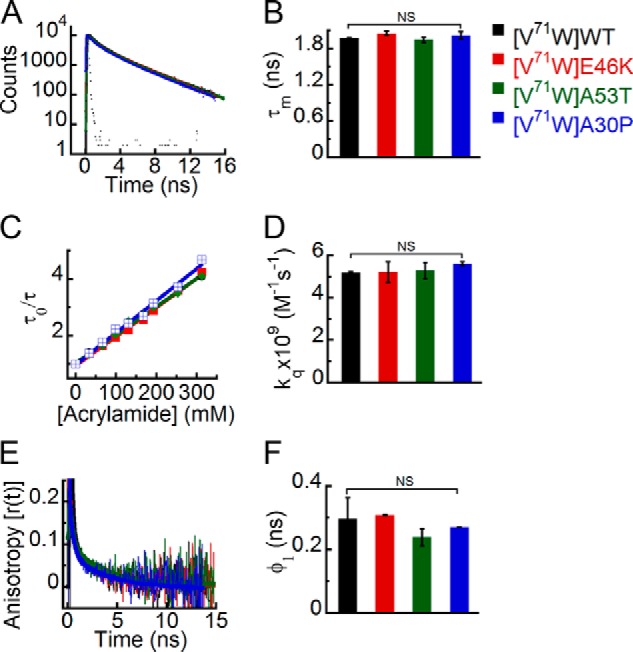
Effect of PD-associated mutations on the site-specific structural dynamics of α-Syn at its middle NAC region (Trp71). Freshly prepared low molecular weight solutions of Trp71 mutant of WT, E46K, A53T, and A30P α-Syns were studied using different fluorescence methods. A, time-resolved fluorescence intensity decay kinetics showing similar decay of fluorescence intensity from Trp71 in WT α-Syn and its PD mutants E46K, A53T, and A30P. B, mean fluorescence lifetime derived from the fluorescence intensity decays kinetics (mean ± S.D., n = 3) showing a similar microenvironment experienced by Trp at position 71 of all α-Syns (WT, E46K, A53T, and A30P). C, Stern-Volmer plots derived from dynamic quenching of fluorescence using lifetime measurements showing that Trp71 in WT α-Syn and its PD mutants E46K, A53T, and A30P have similar slopes. D, the bimolecular rate constants for dynamic quenching (kq) (mean ± S.D., n = 2) showing a similar extent of solvent exposure of Trp71 in WT α-Syn and its PD mutants. E, time-resolved fluorescence anisotropy decay kinetics showing similar anisotropy decays of Trp at position 71 of all α-Syns. F, rotational correlation times (φ1) derived from the fluorescence anisotropy decays (mean ± S.D., n = 2) reflecting similar conformational flexibility of Trp at position 71 of all α-Syns. The statistical significance is as follows: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; NS, not significant, p > 0.05. Error bars represent S.D. The color code shown on the right-hand side (top) in the figure indicates different α-synuclein Trp mutants.
