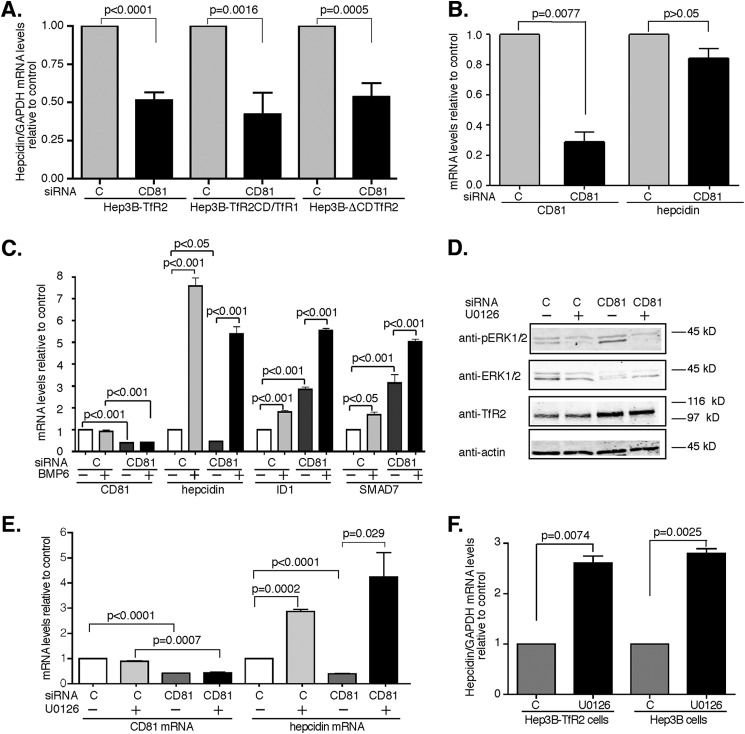
FIGURE 7.
CD81 and TfR2 are both required for the regulation of hepcidin. A, knockdown of CD81 decreases hepcidin expression in Hep3B-TfR2, Hep3B-TfR2CD/TfR1-f, and Hep3B-ΔCDTfR2 cells. The mRNA levels of hepcidin in the cells transfected with control siRNA (lane C and column C) or CD81 siRNA for 48 h in Fig. 2 were measured by qRT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH. Hepcidin mRNA in response to knockdown of CD81 was normalized to that of control siRNA-treated cells. The experiments were repeated at least four times with similar results. B, knockdown of CD81 does not affect hepcidin expression in Hep3B cells. Hep3B cells were transfected with control siRNA (lane C and column C) or CD81 siRNA for 48 h. The mRNA levels of CD81/GAPDH and hepcidin/GAPDH were analyzed as described in A. The experiments were repeated twice with similar results. C, CD81 does not regulate hepcidin expression through BMP/SMAD signaling pathway. Hep3B-TfR2 cells (100 mm dish) were transfected with control siRNA or CD81 siRNA for 24 h and then split into a 6-well plate and grown overnight. The cells were then treated with or without 10 ng/ml BMP6 for 6 h. The mRNA levels of CD81, hepcidin, ID1, and SMAD7 were measured by qRT-PCR, normalized to GAPDH, and then expressed as the ratio of that of control siRNA-transfected cells (lane C and column C) in the absence of BMP6. The graph shows the average data from four independent experiments. D, knockdown of CD81 increased the levels of phospho-ERK1/2. Hep3B-TfR2 cells transfected control siRNA or CD81 siRNA for 32 h were treated with DMSO or 10 μm U0126 overnight. p-ERK, total ERK1/2, TfR2, and actin were detected by immunoblot analysis. E, U0126 increased hepcidin expression independent of CD81. CD81/GAPDH and hepcidin/GAPDH mRNA levels were normalized to control siRNA-DMSO-treated cells. The experiments in D and E were done in duplicate and repeated twice with similar results. F, U0126 increased hepcidin expression independent of TfR2. Hep3B and Hep3B-TfR2 cells were treated with DMSO (lane C and column C) or 10 μm U0126 for 4 h. The hepcidin/GAPDH mRNA levels were normalized to DMSO-treated cells. F, U0126 increased hepcidin expression independent of TfR2. Hep3B and Hep3B-TfR2 cells were treated with DMSO as a control (lane C and column C) or 10 μm U0126 for 4 h. The hepcidin/GAPDH mRNA levels were normalized to DMSO-treated cells.