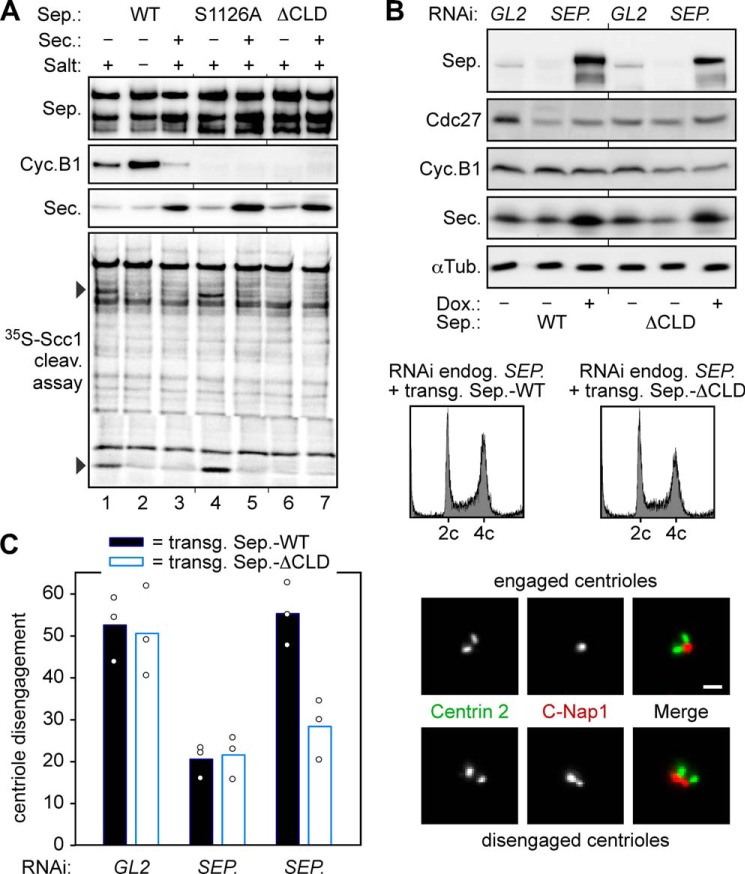
FIGURE 4.
Positive and negative effects of Cdk1-cyclin B1 define the minimal requirements of separase regulation in mitosis. A, WT separase and mutants S1126A and ΔCLD exhibit some, high, or no cohesin cleavage activity upon isolation from prometaphase-arrested cells, respectively. Taxol-treated HEK293T cells transiently overexpressing securin (Sec.) and/or Myc6-TEV2-tagged WT separase (Sep.), S1126A, or ΔCLD were lysed and subjected to anti-Myc immunoprecipitation without prior centrifugation to avoid the removal of insoluble separase fractions. Where indicated, separase-associated Cdk1-cyclin B1 (Cyc.B1) was washed away with a high salt buffer. TEV protease-eluted separases were analyzed by immunoblotting and 35S-labeled Scc1 cleavage assay/autoradiography. B and C, in ΔCLD-expressing cells, the short half-life of proteolytic activity correlates with reduced centriole disengagement. Transgenic HEK293 cells transfected with separase or GL2 siRNA were thymidine-arrested and, where indicated, induced to express WT separase or ΔCLD. Cells were harvested 16 h after release into fresh medium and analyzed by immunoblotting, propidium iodide flow cytometry (B), and immunofluorescence microscopy of purified centrosomes (C). Fixed centrosomes were co-stained for centrin-2 and C-Nap1. Depending on a centrin-2 to C-Nap1 signal ratio of 2:1 or 2:2, centrioles were classified as engaged or disengaged, respectively. In three independent experiments (dots), the engagement status of at least 200 centrosomes per cell line and condition was analyzed and blotted as mean values (bars). Scale bar = 1 μm. αTub., α-tubulin; Dox., doxycycline.